Teacher’s Information Management System Capstone Project Document
Background of the Study
Information is that which informs. In other words, it is the answer to a question of some kind. It is thus related to data and knowledge, as data represents values attributed to parameters and knowledge signifies understanding of real things or abstract concepts. [1] It is valuable in perspective profession of a person. And it serves as their identity in their day to day job/s and transaction/s. It is also a personal property of every individual that must kept efficiently and securely. Information can be encoded into various forms for transmission and interpretation (for example, information may be encoded into a sequence of signs, or transmitted via a sequence of signals). It can also be encrypted for safe storage and communication. [2]
The advancements of modern technology are actually making us safer—not only can new forms of password protection help to safeguard our digital files and documents, advances in voice recognition and gesture control also create a heightened degree of security for our devices and homes. [3] The rapidly increasing technology including a global network has allowed educators the opportunity to create, communicate and store information in incredible ways. Decades attempts have been made to develop systems which make information more precise, readily available and easily accessible throughout the organization. The development and use of information systems is a modern trend which is primarily concerned with the collection, process and dissimilation of useful information that directs an organization for better planning, better decision making and ultimately the better results. [4]
With all of this wonderful technology available, there are several security concerns that arise. Our society is undergoing a process of rapid change, moving toward what is called the information society, intelligent society, knowledge society, network society, knowledge-based society or learning society. The main driver of this change is the growing use of information and communication technologies (ICT’s). The requirement to respond positively to change and to manage it effectively has never been so urgent.
In the case of the teachers, information theft is the rampant incidence and scenarios that happen nowadays. It is the primary concern of every school on how every teacher protect their personal information from theft. Commonly, using of public or rented computers when doing their personal information form is mainly the cause of information theft. However, there is a lot of invention that concerning the information theft incidence but the crime continuously arising.
Another problem rolls out, doing the teachers personal data sheet was done manually.
As an answer to this problem, the researchers develop a Teacher’s Information Management System which could help to process the data/s scientifically. In this system, the teacher/s would no longer record their data/s manually and they can secure their data/s from theft. Also, it will help the teacher/s lessen their time and effort in managing their data/s.
Objectives of the Study
This study aim to develop a Teacher’s Information Management System for the teachers of Buenavista National High School.
Specifically, the study aim to:
- Develop a Teacher’s Information Management System that will be use to:
- Record personal information by creating a teacher’s personal information module;
- Record the family background by creating teacher’s family background module;
- Record the educational background by creating teacher’s educational background module;
- Record the civil service eligibility by creating teacher’s eligibility civil service background module;
- Record the work experience by creating teacher’s work experience background module;
- Evaluate the Teacher’s Information Management System based on ISO 25010 for Software Quality Standards.
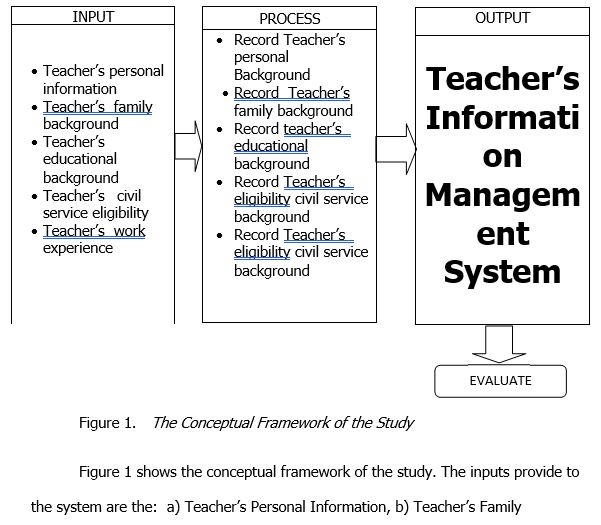
Background, c) Teacher’s Educational Background, d) Teacher’s Civil Service Eligibility, and e) Teacher’s Work Experience.
As for the process, the input will be handled by the components. As shown in Chapter III, a sub process deals with the Upkeep and Management of teacher’s personal information which include the teacher’s surname, first name, middle name, date of birth, sex, civil status, height, weight, blood type, GSIS ID No., PAG-IBIG ID No., PHILHEALTH No., SSS No., TIN No., agency employee no., citizenship, residential address, permanent address, telephone no., mobile no., and e-mail address. A separate sub process for teacher’s family background is also incorporated into the system. These records include spouse’s surname, first name, middle name, occupation, employer/business name, business address, telephone no., father’s surname, first name, middle name, mother’s maiden name, surname, and first name. For teacher’s educational background contains the level of education, name of the school, basic educational/degree/course, period of attendance, highest level/unit earned, year graduated and scholarship/academic honors received. The teacher’s civil service eligibility entails careers service, rating, date of examination, place of examination/conferment, license number and date of validity. The work experience includes inclusive dates, position title, department/agency/office/company, monthly salary, salary/ job/ pay grade, status of appointment and government service.
The overall output refers to the Teacher’s Information Management System that is subject to the evaluation through ISO 25010 Software Quality Standard.
Definition of Terms
For the purpose of clarity, the terms uses in this study are define conceptually and operationally.
Teacher. It is a person who helps others to acquire knowledge, competences or values. [5]
In this study, teacher refers to the subject and respondent of this study which the system will be made.
Information. Facts provided or learned about something or someone. [6]
In this study, information refers to the data/s of the teachers which they will be input in the Teacher’s Information Management System.
Management. Management includes the activities of setting the strategy of an organization and coordinating the efforts. [7]
In this study, management refers to the process which the Teacher’s Information Management System will be executed.
System. A group of related parts and data that move or work together to produce an output. [8]
In this study, system refers to the tool or instrument which the researchers made to provide an efficient way in managing the teacher’s information.
Significance of the Study
This study is very significant and can benefit the following stakeholders:
Teachers. This study will be beneficial to the teachers as the Teacher’s Information Management System will help to manage and secure their data/s to avoid data/s redundancy and theft.
Also, the result of this study will help to lessen the times and efforts of every teacher in doing their personal data sheet to convert into computer-generated through this system.
Schools. This study will be useful to the school which is Buenavista National High School as they will have an idea and information in managing and securing the information of the teachers.
Also, the result of this study will be able to utilize and apply the specific way on how to manage the teacher’s information.
Programmers and Software providers. This study will enable programmers and software providers to utilize technology that can be customized to the needs of the local industry and can be made available to the teachers.
Future Researchers. This study will provide future researchers the information that is significance in the conduct of similar studies.
Scope and Limitation of the Study
The study is limited only to the design and development of the Teacher’s Information Management System for teachers of Buenavista National High School.
This system was limited only to the data of every teacher of Buenavista National High School.
To achieve the desire system performance, it is assumed that there is sufficient input data. Therefore, the accuracy of the system is primarily dependent on the amount of input data.
The initial implementation of the system is a standalone desktop application.
Chapter 2
Review Of Related Literature
This chapter presents a review of related literature and studies. These include a critical analysis of the relationship among different works, and explain the facts, designs, principles and prior arts to which the Teacher’s Information Management System is related.
International Information Systems
International information systems are still a minority interest in the wider field of information systems research. The ABI/INFORM database lists 32,919 papers
(with ‘information systems’ as a keyword) for the period from the beginning of 1985 to the end of 2005. For the same time period, keywords to do with international information systems occur in 2341 papers, i.e. in less than 1%. By contrast, a traditional sub-area of information systems research such as Decision Support Systems has 3,607 listings in the last 15 years, or 11% of all IS papers. When the current research was started towards the end of 1994, there were a total of 69 papers listed for the 10-year period 1985–1994 – only 14 of them. [9]
Dynamic International Information Systems
International information systems are still a minority interest in the wider field of information systems research. The ABI/INFORM database lists 32,919 papers
(With ‘information systems’ as a keyword) for the period from the beginning of
1985 to the end of 2005. For the same time period, keywords to do with
International information systems occur in 2341 papers, i.e. in less than 1%. By
contrast, a traditional sub-area of information systems research such as Decision
Support Systems has 3,607 listings in the last 15 years, or 11% of all IS papers.
When the current research was started towards the end of 1994, there were a total
of 69 papers listed for the 10-year period 1985–1994 – only 14 of them in ‘1st
Tier’ journals.2 Interest then seems to have increased and over the next 5 years 165. [9]
Information System Integration
In the information systems field, integration has been viewed from two perspectives in information system. A technical standpoint in the first perspective suggests that integration is a mechanism to depict the interconnectedness of information technologies within an organization and the extent to which a common conceptual representation of data elements are shared. In other words, integration is defined as the degree to which different systems of an organization are interconnected and are capable of communicating to each other (e.g. islands of technology integration).
In the second perspective, integration is the degree to which two or more independent organizations have standardized business processes and those processes are firmly linked through telecommunications technologies and computers
Information system integration aims at facilitating exchange and information sharing within an organization, and achieving inter-firm coordination (between buyers and sellers) for better monitoring capability as in the case of supply chain. In regard to technological integration, it has been repeatedly stressed that information system integration needs all application systems, data, and communication to be integrated in order to provide a real-time and consistent connectivity within function component across supply chains.
Linß and Rosemann classified integration into three main dimensions encompassing: domain, reach, and direction. Accordingly, direction is either horizontal or vertical; reach is either intra-organization or interorganization, and domain is either data-wise, function-wise and, program-wise. It should be added that Rosemann considers object-wise as another sub-dimension for domain. While Picot, Reichwald, & Wigand categorized it as ex-ante and ex-post integrations, in addition Fuchs-Kittowski grouped ex-ante integration into re-engineering and integrated components, and on the other hand classified ex-post integration into sub-dimensions as data, function, and presentation.
Regardless, it has been equally emphasized in many information systems literature that information system per se is not a source of sustainable performance and value creation. Consequently, integrating resources and aligning them in organization’s cultural and social context is crucial, in particular, in developing workflow and operations coordination. In sum, integration per se has been found to be a sociotechnical phenomenon beyond a mere technological aspect such that it includes an assortment of economical, organizational, and even social facets
of the phenomenon. [9]
Below we describe other forms of integration as evident in information systems literature:
Strategic integration
This integration is about whether different integrated systems are supporting an organization’s core strategic plans. In this manner integration is not considered as goal by itself, though, it should be rather identified as a means to achieve the central strategic directions of the organization.
Horizontal integration
Horizontal integration is evident in manufacturing function and coordination
amongst them. Horizontal integration is concerned with how easy decisions are made and data are passed among the islands of technology as well as the degree to which they are collaborating, coordinating, and facilitating task performance.
Vertical integration
This form of integration enables access to information visit the website at various levels of the organization hierarchy, in particular, for managers and decision makers.
Electronic integration
Zaheer & Venkatraman first introduced it as a form of vertical quasiintegration. Thus, deploying computers and communication systems among relevant actors in adjacent stages of value chain are the means to achieve electronic integration. In fact, its focus on the role of IT in restructuring vertical relationships,
has made it an important concept in information research. From organizational integration perspective, vertical integration is concerned with a firm covering two single output production processes in which all or part of the upstream output processes are employed as either entire or part of intermediate input into the downstream processes.
It also involves internal integration (units linked within firm) and external integration (links among firm with customers, suppliers and retailers). For instance, e-procurement which reflects the transactional nature of using IT in supply-chain
context, is one aspect of electronic integration that represents the operational aspect of sourcing over information technology enabled platforms.
Communication network integration
Agents deploy integrated communication networks by transmitting information around the globe in structured data, text, visual forms or audio format, via flexible standards including satellites, cable or fibers. Such electronic inter-connectivity between organizations would be expected to cut costs and enhance services and efficiency through tightening inter-relations. This is also needed for
organization to coordinate internal activities in an effective and efficient manner toward attaining competitiveness .
Steinbart & Nath have also emphasized the essential role of standards and
network connectivity. In addition, the lack of standardization of key technologies that support network connectivity is one major factor that impedes prompt responses of information systems
Physical integration
Physical integration works on supporting and encouraging cooperation between several departments or production facilities of an organization which are dispersed in various geographical zones.
Data integration
Data integration focuses on the degree to which the activities of different business units and departments within an organization are consistently coordinated by sharing a number of databases. Organizations could initiate developing systems integration by enhancing standardization of data codes and definitions throughout the organization or on a larger scale of the industry. Wendt, Brigl, & Winter propagates data integration as enabling users to enter data only once in several application components, e. g. patient identification data.
Temporal integration
Provides access to historical data or information in order to facilitate efforts of
future planning process.
Semantic integration
Semantic integration refers to when several application components using the
same data also use or provide the same concept system, e. g. the same diagnosis classification system, for interpreting data.
Context integration
Context integration refers to when several application components are synchronized automatically with regard to context descriptors like user login or patient identification data.
Presentation integration
Presentation integration refers to when several application components used
by the same users provide equally designed user interface elements for equal presentation and interaction functions.
Process integration
Process integration involves the minimization of communication and coordination effort between activities of a process.
Electronic data integration
This refers to complex integration to many internal applications
using many different protocols over LAN and WAN.
Specification integration
This type of integration shares the similar characteristics by those of middleware integration, internal integration, and level-1 integration [39]. This integration is related to providing the specifications of system technical design at the hardware, software, and Mathematics and Computers in Contemporary Science
ISBN: 978-960-474-356-8 71 application level of stand-alone. This type of integration works on a minimum specification of any information system and that needs minimum computer hardware.
Compatibility integration
Integration could be achieved by satisfying the level of compatibility
between different system components. Human resource plays an integral role in compatibility integration.
Ergonomic integration
Ergonomic integration is concerned with users’ comfort with graphical interface, software, keyboard, and hardware. User friendliness and environmental consideration are also within ergonomic integration.
Cognitive integration
Intangibility, usefulness, and consistency of communication between user and system are referred to as cognitive integration. Besides, it covers communication encompassing error messages and other related information. [10]
Methodology
This chapter presents the project description, design specification, project development, project evaluation, data gathering instrument, validity of instrument, respondents of the study and data analysis procedure and statistical treatment of data.
Project Description
The development of Teacher’s Information Management System is the main deliverable of the proponent’s study conducted at Buenavista National High School in New Poblacion, Buenavista, Guimaras, Philippines. The data/s of the teachers has been the most important aspect of the system’s conceptualization and development. Such data will be invaluable when it comes to manage and secure the data/s. Furthermore, sufficient data of the said system was also use to lessen the times and efforts of a teacher in managing and securing their valuable data/s and record/s.
System Architecture
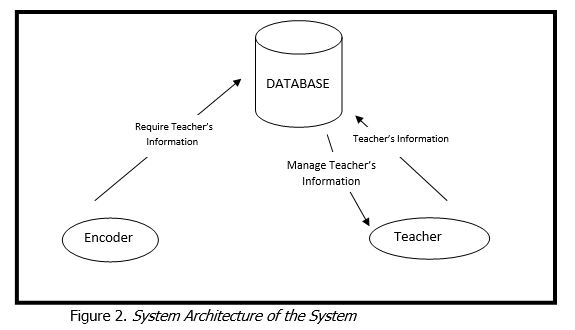
The researcher identified the necessary data, components, and functionalities which established the architecture of the system as shown in the figure 2.
The system can be used by the two types of users, each have a corresponding modules for the desired task and functionality. Starting with the Encoder, the encoding process records teachers data which includes the personal information, family background, educational background, civil service eligibility, work experience, voluntary work or involvement in civic, learning and development (l&d) interventions/training programs attended, references , government issued ID and other necessary information that would comprise the teacher’s profile.
The second type of user that interacts with the system is the Teacher. The Teacher is responsible for supplying the required data/s which encoder input on the system. The database will give or produce an output which the system manage the teacher’s information.
Design Specification
Design Specification describes all data, architectural, interface and component-level design for the software.
The following design specifications are described to illustrate the development of the proposed system.
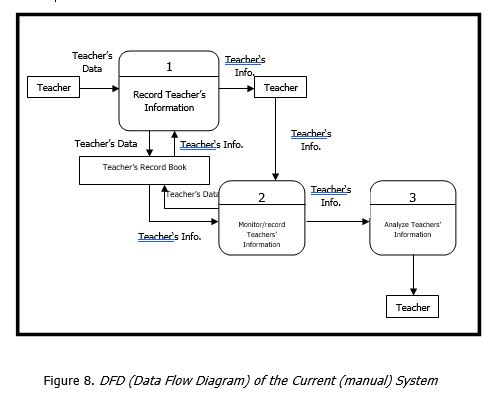
Data Flow Diagram
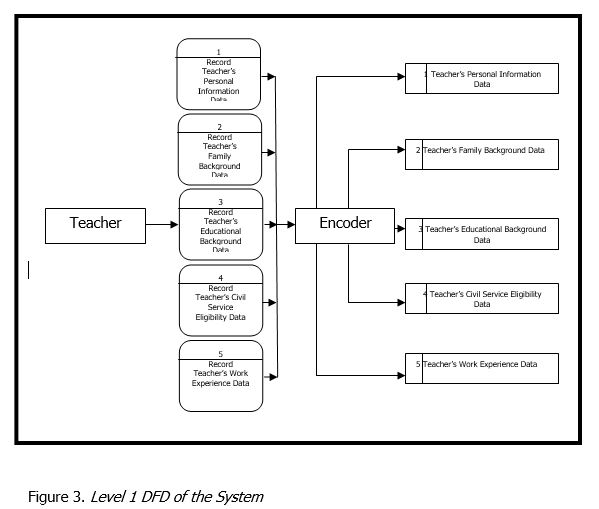
A data flow diagram (DFD) is a graphical representation of the “flow” of data through an information system, modeling its process aspects. A DFD is often used as a preliminary step to create an overview of the system without going into great detail, which can later be elaborated. DFDs can also be used for the visualization of data processing (structured design). A DFD shows what kind of information will be input to and output from the system, how the data will advance through the system, and where the data will be stored. It does not show information about process timing or whether processes will operate in sequence or in parallel, unlike a traditional structured flowchart which focuses on control flow, or a UML activity workflow diagram, which presents both control and data flows as a unified model. The Level 1 DFD of the system is shown in figure 3.
Use case Diagram
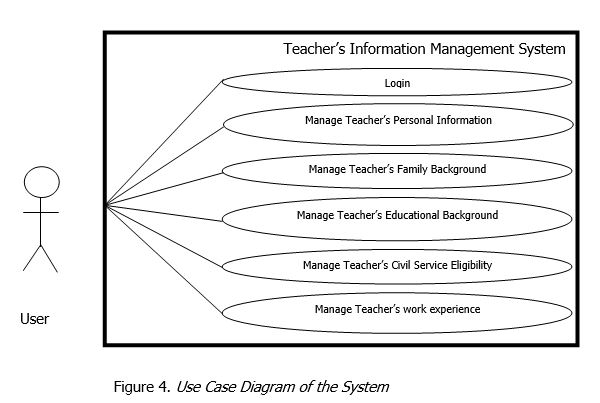
A Use Case Diagram is a representation of a user’s interaction with the system that shows the relationship between the user and the different use cases in which the user is involved. A use case diagram can identify the different types of users of a system and the different use cases and will often be accompanied by other types of diagrams as well. Primarily, a use case itself might drill into a lot of detail about every possibility; a use-case diagram can help provide a higher-level view of the system. It has been said before that “Use case diagrams are the blueprints for your system”. They provide the simplified and graphical representation of what the system must actually do. The purpose of the use case diagrams is simply to provide the high level view of the system and convey the requirements in layman’s terms for the stakeholders. Additional diagrams and documentation can be used to provide a complete functional and technical view of the system.
In figure 4, the Use Case Diagram of the system is shown. Generally, the Encoder and the teacher/s. As an encoder, the role is to record the Teacher’s Profile, handled grades and section by encoding the required data. As a teacher, the role is supply the require data/s of the system. The process makes use of the generic data provided in order to input individual record of each teacher. These data are specifically important when it comes to generating teacher’s information. In relation to that, the user is able to manage a teacher’s data by keeping the record up to date by encoding the latest data/s of the teacher/s.
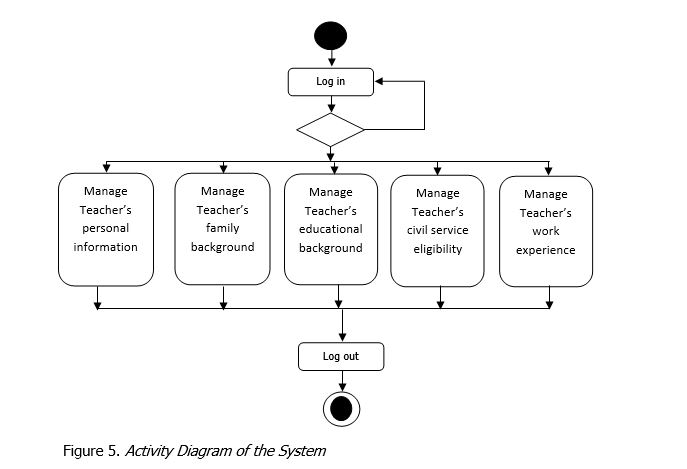
Activity Diagram
An activity diagrams are graphical representations of workflows of stepwise activities and actions with support for choice, iteration and concurrency. In the Unified Modeling Language, activity diagrams are intended to model both computational and organizational processes (i.e. workflows). Activity diagrams show the overall flow of control. Activity diagrams are constructed from a limited number of shapes, connected with arrows. Activity diagrams may be regarded as a form of flowchart. Typical flowchart techniques lack constructs for expressing concurrency. However, the join and split symbols in activity diagrams only resolve this for simple cases; the meaning of the model is not clear when they are arbitrarily combined with decisions or loops.
In figure 5, the Activity Diagram of the system is shown. The result needs to log-in before it access to record the teacher’s personal information, family background, educational Background, civil service eligibility and work experience. Thos data are used for generating the teacher’s information. Once the tasks are done, the user can log out of the system.
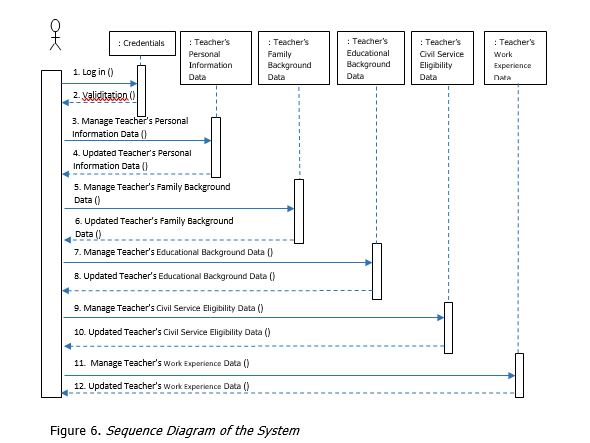
Sequence Diagram
A sequence diagram is an interaction diagram that shows how objects operate with one another and in what order. It is a construct of a message sequence chart.
A sequence diagram shows object interactions arranged in time sequence. It depicts the objects and classes involved in the scenario and the sequence of messages exchanged between the objects needed to carry out the functionality of the scenario. Sequence diagrams are typically associated with use case realizations in the Logical View of the system under development. Sequence diagrams are sometimes called event diagrams or event scenarios, as shown in Figure 6.
During the log in, the user provides the credentials for validatation. After each, the user is given access to the Teacher’s Data which enables in return keeps the said data updated.
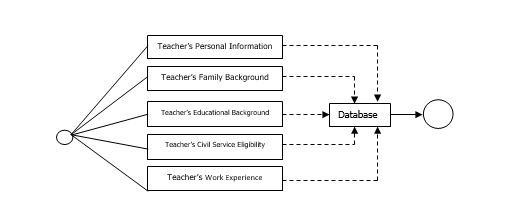
Deployment Diagram
A deployment diagram in the Unified Modeling Language models the physical deployment of artifacts on nodes. Nodes could be connected through communication paths to create networked systems of arbitrary complexity. It shows the execution architecture of systems that represent the assignment deployment of the software artifacts to deployment targets. The diagram show components and relationships between components and classifiers, and deployment diagrams – deployments of artifacts to deployment targets, some missing intermediate diagram is manifestation diagram to be used to show manifestation (implementation) of components by artifacts and internal structure of artifacts. The importance of deployment diagrams is used to handle logical components but deployment diagrams are made to focus on the hardware topology of a system.
Figure 7 shows the deployment Diagram of the system. The system composed of a database and various components which perform respective functions that users interact with. All information of a teacher/s provides as input to its respective modules; all of which are stored and searchable in a database.
In order for the system to run smoothly, the necessary hardware requirements should be met. In Table I, the minimum hardware specification is shown. Although the specification is sufficient to run the system, increasing it would significantly affect the execution of the system, thus improving the overall performance and user experience.
Hardware Specification
| Type and Model | Specification |
| CPU Type Model | Dual Core 2.3 GHz or Higher |
| Storage Type | 500GB Disk or Higher |
| Input Device | Mouse and Keyboard |
| Output Device | Monitor and Printer |
In Table II, the software specification of the system is shown. As for the software components of the system, it was built
Software Specification
| Operating System | Microsoft Windows 7 or Higher |
| Programming Software | |
| Database | Absolute Database |
Project Development
During the planning phase, the researchers determined the current problem of a teacher. Several problems have been discovered. These include the high demand of manual recording, unprocessed data and absence of data analysis crucial for teacher’s information decision making.
After the problems had been identified, the researchers thought of creating a system to help the teachers in their dilemma of manually recording of the teacher’s data. The system includes features on the development of module for teacher’s profiling. In this system, the manual recording, unprocessed data and absence of data analysis crucial for decision making will be addressed.
In the Analysis Phase, it is important that the current system be studied in order to expose the actual needs of the client as well as the problem that need to e addressed. By doing so, the researchers can produce a system design that is tailor-built for the long standing principles and workflows of the teacher’s data/s, thus producing the desired system output.
Figure 8 present the data flow diagram of the present system. In the said system, everything is done manually wherein the recorder of the teacher’s data/s on a teacher’s record book. Then after recording raw data, the encoder will monitor and record the present teacher’s data/s. After which, the encoder will analyze data after through monitoring. Upon the analysis of the present approach of the data/s monitoring, a new modeled (as shown in the proposed system’s DFD). The design of the system is based on what was observed on the actual workflow of the teacher’s information.
Project Evaluation
The system was tested for accuracy, precision and recall. Also, the system’s quality was tested if conforms to that ISO 25010. This sets the standards on the software’s functionality suitability, reliability, performance efficiency, operability, security, compatibility, maintainability and portability. The method of assessment was conducted by calculating the mean of each quality characteristic.
Data Gathering Instrument
The data requirements of the system ware gathered through interviews, article reviews and reading of previous studies. Accordingly, the researchers used the quantitative method. After which, the data were filtered by taking the simplest requirements for the development of the system.
The feedback on the system’s performance was gathered by conducting a system evaluation which was done through system accuracy survey and system’s quality evaluation survey.
Validity of the Instrument
Questionnaires are the most frequently used data collection method in educational and evaluation research. Questionnaires help gather information on knowledge, attitudes, opinions, behaviors, facts, and other information. Validity is the extent to which an instrument measures what it is supposed to measure and performs as it is designed to perform.[10]
The quality assessment of the system was based in ISO 25010 International Quality Standards. The survey instrument is considered valid since it is pre-validated by the above mentioned organization prior to its use and implementation.
Results And Discussion
This chapter represented the development of the systems, evaluation of the system’s accuracy by the teachers and IT experts of the system’s output and overall operating performance in terms of functional suitability, performance efficiency, compatibility, usability, reliability, security, maintainability and probability.
Development of the System
The Teacher’s Information Management System is the output of the proponent’s study conducted at Buenavista National High School in Barangay New Poblacion, Buenavista, Guimaras. The software is provided with years’ worth of data that include the teacher’s personal information, family and educational background, civil service eligibility and work experience. The above mentioned data were gathered, processed and analyze in order to come up with the reliable forecast abd efficient management of teacher’s information.
Figure 10 shows the Log in form of the system. Wherein it serves as the security engine of the system. This is where the users select the username which they will used and provided password, and if validated provides with credentials to access the system.
Summary, Conclusion And Recommendation
This chapter presents the summary of finding, the conclusions that were drawn from the findings and the recommendations to further enhance the system for future researchers.
Summary
In this study, the Buenavista National High School Teacher’s Information Management System was developed by the proponents for the teachers of Buenavista National High School in New Poblacion, Buenavista, Guimaras, Philippines. As primary output, the software is provided with the data that includes teacher’s personal information, family background, educational background, civil service eligibility and work experience. In order to come up with reliable data and efficient management of teacher’s records, the aforementioned data were gathered, processed, and analyzed.
Conclusion
- The system was implemented and evaluated in terms of functional suitability, performance efficiency, compatibility, usability, reliability, security, maintainability and probability.
The Buenavista National High School Teacher’s Information Management System presented in this study was able to:
- Record the teacher’s personal information;
- Record the teacher’s family background;
- Record the teacher’s educational background;
- Record the teacher’s civil service eligibility and;
- Record the teacher’s work experience.
- The Buenavista National High School Teacher’s Information Management System is very functional, suitable, reliable, performance efficient, usable, secured, compatible, maintained, and portable. This means that the system has strong manifestations that it is complaint with the required features of a decision support system in accordance with known practices and standards.
Recommendations
From the study’s findings and conclusions, the researcher recommends the following:
- It is recommended that the Buenavista National High School Teacher’s Information Management System be implemented in order to improve the management procedures and recording of teacher’s data as well as to address the problems encountered with the existing system.
- The Buenavista National High School Teacher’s Information Management System should be enhance when it comes to error-free system, user friendly graphic interface and flexibility.
- The Buenavista National High School Teacher’s Information Management System should be print directly in order to fasten the time where to consume in undirect printing.
- And the Buenavista National High School Teacher’s Information Management System should be widening its scope when inputting the data’s.




Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.