Computerized Student Information System Capstone Project Document
Introduction
Student information system as of study today is changing what people is learning upon such as with the burgeoning of the internet , the control exercised in the past by the Philippines from various departments of education and by individual teachers over pedagogical content may have diminished significantly. Through this new informative medium, resources of varying quality and provenance on virtually diverse subject matter are now available to the students. Truly, it is crucial to the advancement of informative research within composed disciplines and the continued successful integration of SIS applied in the Philippines setting with resources to higher education systems determining to that certain group of students can acquire and gain effective knowledge literacy skills through the SIS process and understanding the value of education services crafted to provide the best teachings as possible. The SIS encourage the use of SIS in parallel to define learning style which allows students to interact with their classmates and does help the instructor facilitate on enhanced learning experience through SIS application mode and to finally emphasize the value of making student information connection with a subject teacher for instance geared upon for in depth education success.
Many schools that were established in Isabela are still using the manual based system up to present. In managing their systems, they have encountered difficulties and problems like slow transaction, redundancy of data and unsecured files. Based on these problems encountered in the present system, the researchers came up with the proposed ISU-E laboratory high school student information system which is generic in nature, and will be used by different schools in the entire province. The system is to provide reliable data and to make the tasks easier.
The proposed computerized system will provide accurate, fast and simplified process to accomplish the transaction of the school. The school gains benefits for having a computerized system by having more improvements to the daily transaction and for the accomplishments of tasks. Also the proposed system aims to solve and conditions in the present system. It will also produce timely documents and reports, provide minimal problem, solving information, integrate data form multiple files, perform necessary tasks, reduce errors, retrieve data and information rapidly, reduce data redundancy and maintain a high degree of accuracy and integrity.
The researchers made use of different methods in developing the system. The methods are the methods of system development which composed of hardware and software in the development of the system, the methods of software testing is done in order to eliminate errors during the program cycle execution and the methods of software implementation where researchers used the parallel method.
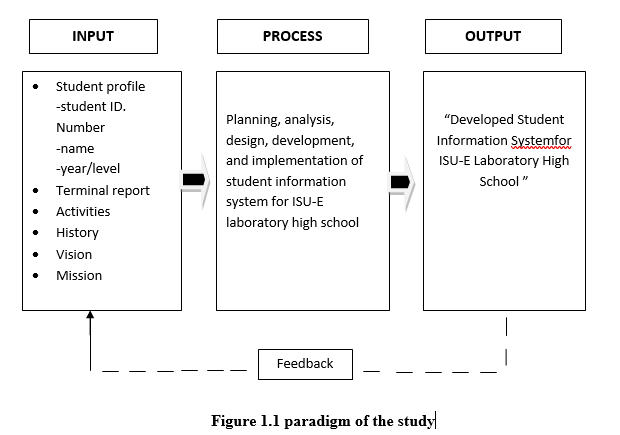
Conceptual framework
The illustration below shows the input, process and output of the study. It illustrates that before arriving into a good output, the researchers should widen their analysis regarding the operations of the present to the study of problems that are being encountered by the agency in order to formulate, generate and create alternative solutions to the problems and to arrive into the designed output.
Statement of the problem
The researcher’s main focus is on the development of the proposed student information system for ISU-E Laboratory High School. It aims to determine the problems that the school is experiencing with its present system so that the researchers can come up with measures to improve it. Specifically, the study seeks to answer the following:
- What are the existing problems encountered in the present system?
- How will the present system be designed, developed, and implemented?
- Will the implementation of the new computer based system improve the present system?
- Will there be a significant difference between the present system and the proposed system?
Statement of objectives
- To be able to evaluate the proposed system in terms of user acceptance.
- To be able to evaluate the proposed system in terms of security and accuracy of reports.
- To be able to evaluate the proposed system as a solution regarding to the problems of students records.
- To be able to evaluate the efficiency of the proposed system in terms of saving time ,exerting effort and deducting the burden of the students.
Significant of the Study
The proposed study intended to evaluate the manual based system of keeping records of ISU-E laboratory high school and eventually to upgrade its operation in order to facilitate be able to recognize pertinent information of students. This study was conducted for the benefit for the school, students, researchers and future researchers as well.
The School. The proposed system is intended for the school of ISU-E Laboratory High School, which is more improving delivery of service especially in the registration and assessment of fees, recording and verification. This study leads to the development of a computerized information system in the most practicable way.
The Students. The development of the system is to lessen the burden in registration and assessments of the students through the computerized student information system.
The Researchers.By study, the researchers gain additional knowledge and have the opportunity to develop their skills in system analysis and software development.
The Future Researchers.This study will serve as reference for future researchers. It will serve as a guide on how to conduct such study to do better of necessary.
Scope and Delimitation of the Study
The proposed Student Information System for ISU-E Laboratory High School is generic in nature. The system will only be used when procedures and design of the system to the structure and organization of the proposed system. The study only proposed system covered the period from June 2011 to October 2011.
The study covers the computerization of the students profile record, student enrollment list, students grade records, and also the teacher or staff of the said school information.
The proposed system tested and eventually implemented in the school of Isabela State University Laboratory High School Echague campus, particularly researchers test and implement the proposed system in the student information system.
The proposed computerized system composed of three(3) users; the administrator side, the registrar side, and the cashier side. The administrator side system serve as a controller of the entire module, it acts as a server to different modules. It is composed of four(4) main menus; Set Up, Report, Help and Exit.There will be respondents of the proposed system. There were fifty(50) respondents including the students of the said school. The database will be backed up using a separate storage device to be of help in case of something happens to the original storage.
Definition of terms
Some technical and operational terms are hereby defined in order to a better understanding of the study.
Technical terms
Computerized. Refers to storing, processing, analyzing or generating by a computer. (Turban, 1991)
Database. Refers to any collection of data organized for storage in a computer memory and designed for easy access authorized by users.(Turban, 1999).
Documentation. Refers to relation to computers, the set of instructions shipped with a program or a piece of hardware.(Encarta,2003)
Password. Refers to a security measure use to restrict access to computer system and sensitive system files.(Microsoft, 1993-2006).
Record. Refers to retaining information usually in file. (Turban, 1998).
System. Refers to any collection of component elements that work together to perform. ((Microsoft, 1993-2006)
Researchers. Issomebody who performs research,the search for knowledge or in general any systematic investigation to establish facts. (Basha and Harten, 2007)
School. Isan institute designed for the teaching of students (or pupils) under the direction of teachers. (Bolman and Deal, 1991)
Student.Is a learner, or someone who attends an educational institution.(Joe Lagarteja& Rudolf Caesar)
Teacher.Is a person who provides schooling for students or pupils.(Joe Lagarteja& Rudolf Caesar)
Log-in. It is where the system manager log in to access to access the database of the system. (Ewald, 2006)
File.A collection of program instructions or data stored on a hard drive disk, or other storage medium and threatened as a single entity. (Eyffe& Walter,2005)
Help. It provides advice, directions or information to help somebody to do something easier and possible. (Glorielyn Passion &RendelParado)
Record. Is a collection of related items of information treated as a unit by a computer in a database. (JD Edwards,2009)
Enrollment.The process of registering the student.(JoeLagarteja& Rudolf Caesar)
Review Of Related Literature And Related Studies
This chapter presents a number of previous studies and researchers about student information system. It also includes other sources of reference that are perceived to have significant bearing on this study.
Related Literature
Foreign
Systems analysis and design, as performed by systems analyst, seeks to analyze data input or data flow systematically, processing or transforming data, data storage, and information output within context of a particular business. Furthermore, systems analysis and design is used to analyze, design, and implement improvements in the functionality of business that can be accomplished through the use of computerized information systems.[1]
Numerous companies offer different kinds of student information system that is capable of recording and providing access to student information. A kind of student information management system is Chancery SMS by Chancery Software Ltd. Chancery SMS is a web-based solution that runs on the Windows 2000 Server platform. It can be hosted in a central location by a district or a Regional Service Center. Each school site connects to the application through the Internet or Intranet using a standard web browser.[2]
Educational institutions are under constant pressure to demonstrate both willingness and capacity to incorporate the latest developments in student information systems along with communications technology supporting various teaching ways. Asserts that SIS process within such technological sophistication does create precise knowledge edge, that such SIS application can be appealing to students and to the academic faculty as well as the parents. Thus, believing that technology is the repository of the bulk of the information that underpins society’s major enterprises and concerns and the medium of communication through which SIS interact with one another. [3]
Local
Another kind of student information management system would be the Centre by the Miller Group. It includes capabilities such as: Student screens that include all the critical information necessary for reports and decision-making, provide quick access to demographic information, and also assign email addresses, admittance to the system and passwords. [4] These student information management systems are efficient in handling student data, any of which can be utilized by the school registrar of Philippine Science High School – Central Mindanao Campus, but these Student information management systems are only available in countries such as United States of America and Canada and not yet in the Philippines and the purchase of these software will cost a high price.A local variant of a student information system, the Student Record System (SRS) for Philippine Science High School – Central Mindanao Campus (PSHS-CMC), was developed by Taddie Fel L. Dagaerag and company (2002).
SRS was designed to assist the registrar of PSHS-CMC but proper attention for the smooth transition from the previous system to the SRS was not given so the system encountered problems, which require major revisions.[4]
According to the school former registrar, Ms. Shiela M. Preagido (Registrar PSHS-CMC, year 2005), “…report on grade is not that usable, unless another program will be made that can copy grades from the summary grades sheets,” therefore, rendering the SRS unusable for the present. There are still insufficient services offered by any software solutions company in the Philippines that can provide the same kinds of functionality on a system with lower cost compared to foreign products. Such student information system would cost in the range from 75,000 pesos to 150,000 pesos. [4]
Student information system or SIS incurs such application software designed for educational establishments to manage student data. Student information systems provide capabilities for entering student test and other assessment scores, building student schedules, tracking student attendance as well as managing many other student-related data needs within the institution university. Thus, many of these systems applied in the Philippines can be scaled to different levels of activity and can be configured by their home institutions to meet local needs.[3]
Related Studies
Foreign
Texas State University-San Marcos is implementing a fully-integrated student information system (SIS). The ultimate purpose of this project is to provide the University with an information system that will address the current and future needs of students, staff and faculty.The SIS project has a web site with more information for faculty, staff and students.[5]
This survey collected annual information from degree-granting universities and colleges in Canada on individual student characteristics and their study programs including gender, age, citizenship, geographic source of student, field of study, level, type of attendance (full-time/part-time and year of graduation). University Student Information System. [6]
The use of the University of Lapland’s student registry is based on laws and regulations. Based on the laws the university gives out information from the registry without students’ consent to Statistics, The Social Insurance Institution of Finland, Student Health Care Foundation YTHS, Employment Office, Student Union LYY and to scientific research. With the student’s consent and staff’s own consideration the university can give out information from the registry for study related purposes and direct marketing. Release conditions are defined when registering for the first time. Students can also change the release conditions in WebOodi. Release of Information from Student Registry. [7]
Local
“Computerized school registration system of Saint Paul University (2003)” by Philip V. Napapan. This software accepts new enrollees, payments, and generates report. The authors of this software uses MS access for database, OBDC for the connection drivers, and MS excel for the reports.[8]
The MSU Preparatory High School keeps its record manually since it exists for more than forty years now. The procedures followed are so time consuming especially in adding, sorting, editing and locating students’ file. Besides, when the administration generate reports oftentimes entails access to each student file which requires a lot of effort and time.[9]
“High school enrollment system of Dipolog City (2004-2005)” by Vincent J. Jamero. The high school enrollment system is for curriculum based high school institution. It includes registration, students and teachers scheduling, student billing and other high school information management staff.[10]
Synthesis of the Study
The related literature and related studies discusses the importance and concepts of managing records as: creation filing for studies on computerized system. Almost all of the researchers recommend the design, development and implementation of computerized system to facilitate and improve information processes and decision making and changing from a manual system can be minimize if not eradicated. And the quality of service when it comes to accuracy of reports, fast input, and data security can be greatly improved.
The researchers found out that the most permanent problem areas of manual system are slow data processing in accuracy of reports, time consuming, bulky workload, and loss of data.
Research Methodology and Procedures
This presents the methodology used by the researchers in gathering data needed for the accomplishment of the study in order to apply the different methodologies and procedures properly. It will present the following; the research design, data gathering instrument, data analysis tools and development tools.
Research Methodology Tools
The researchers primarily used descriptive method of research to fully expand and understand the flow of data gathered, issues concerning the status of the existing system. The proposed student information system for ISU-E laboratory high school of San Fabian Echague, Isabela, was conducted to design and implementation efficient and secured new system to be designed and implemented.
Development method was used to produce the proposed system. The researchers used the system development life cycle(SDLC) as a tool, model and structured approach to information system development that guides all the processes involved from all its initial study to maintain is finished application.
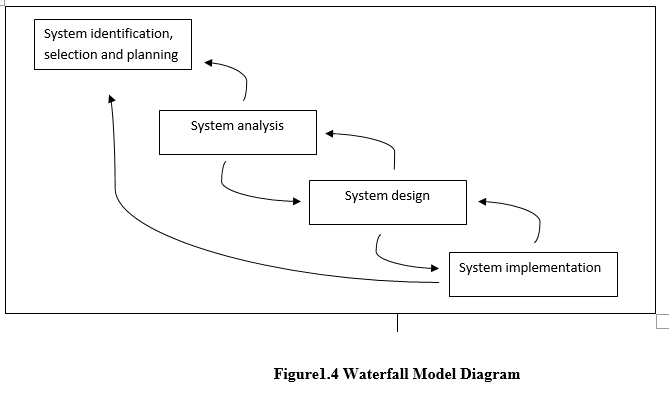
System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Tools
Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a process used by a systems analyst to develop an information system, including requirements, validation, training, and user (stakeholder) ownership. Any SDLC should result in a high quality system that meets or exceeds customer expectations, reaches completion within time and cost estimates, works effectively andefficiently in the current and planned Information Technology infrastructure, and is inexpensive to maintain and cost-effective to enhance. Computer systems are complex and often (especially with the recent riseof Service-Oriented Architecture) link multiple traditional systems potentially supplied by different software vendors. To manage this level of complexity, a number of SDLC models or methodologies have been created, such as “waterfall“; “spiral“; “Agile software development“; “rapid prototyping“; “incremental“; and “synchronize and stabilize”.
Preliminary Phases
The following techniques were used by the researchers in order to gather pertinent data and information necessary in the design and development of the proposed system.
Questionnaire Method.Is a written or printed form of gathering information on some subjects consisting of a set of questions distributed to and filled up by the respondents. Questionnaire method was used to evaluate the overall impact of the proposed system to its benefactor. With the result the researchers were able to confirm that the proposed system is timely implemented.
Interview Methods.The researchers made use of this technique of collecting data in order to verify and confirm information. This is a method where researchers are able to get ideas and comments pertaining to the design and structure of the proposed system. It was also through interview where the researchers were able to understand the tecnhiques and strategies used by the manual system.
Observation Method. This method of gathering data further strengthened the concept of the study. Through this method, the researchers were able to observe the procedures in the traditional method and a computerized system. By this study, the researchers know how the procedures in using the manual based.
Library Method.The researchers visited the library to scan some books, reference and thesis in order to understand better the study and be able to locate some basis in the development of the proposed system.By this study,the researchers were able to gather data and information through the use of library.
Internet Method.The researchers browse through internet sites and other related links in search of valuable information vital for the conduct of the study and additional information regarding the development of the proposed system. By this study the researchers browse through internet to gather some information.
Analysis Phases
- Data
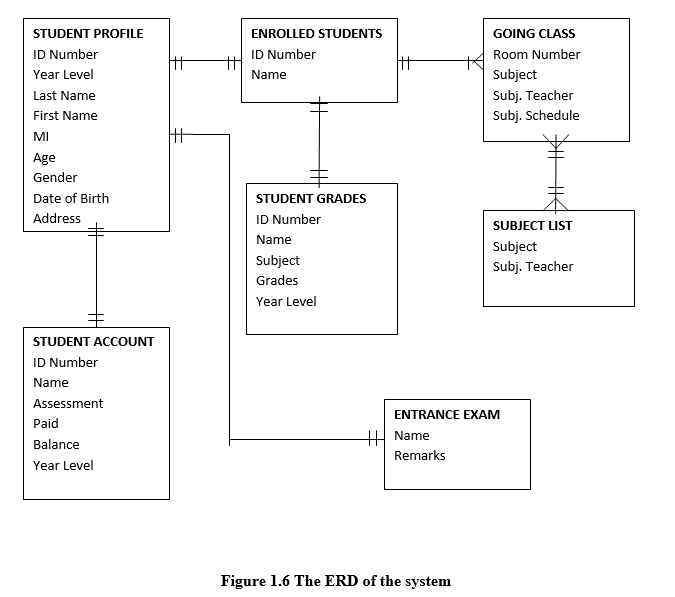
ERD (Entity Relationship Diagram) is a specialized graphic that illustrates the interrelationships between entities in a database.
Data Dictionary
is a tool used to ensure the consistency of all elements in a system.
- Process
DFD (Data Flow Diagram) is a means of representing a system at any level of detail with a graphic network. It also represents the graphical flows of a system using different symbols like external entity, process, repository, and flowlines.
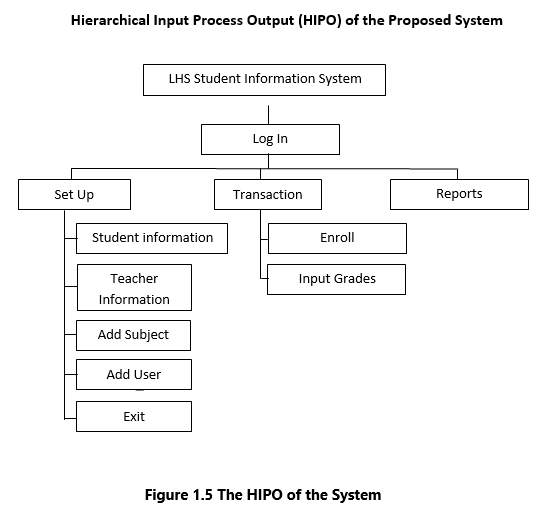
(HIPO)Hierarchical Input Process Output is a tool for planning and/or documenting a computer program that utilizes a hierarchy chart to graphically present the program’s control structure and asset of IPO charts to describe the inputs to the outputs from, and the functions performed by each module on the hierarchy chart.
IPO(Input Process Output) a chart that describes or documents the inputs to,the output from, and the functions performed by a program module.
- Interface
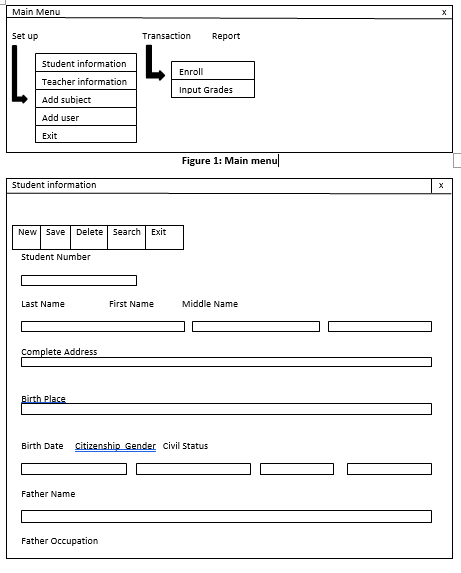
Wireframe also known as a page schematic or screen blueprint, is a visual guide that represents the skeletal framework of a system.
- Result
Lickert Scale method was used to analyze the result of the survey using the formula:
Rating =(SA*5)+(A*4)=(U*3)=(D*2)=(SD*1)
Total number of Respondents
Where:
Rating=total number of respondents
SA= total number of respondents answered Strongly Agree.
A= total number of respondents answered Agree.
U= total number of respondents answered Undecided.
D=total number of respondents answered Disagree.
SD= total number of respondents answered Strongly Disagree.
| Rate | Value | Conversions |
| Strongly Agree | 5 | 4.51-5.00 |
| Agree | 4 | 3.51-4.50 |
| Undecided | 3 | 2.51-3.50 |
| Disagree | 2 | 1.51-2.50 |
| Strongly Disagree | 1 | 1.00-1.50 |
Table 1.2 The Lickert Scale Method
Design Phases
Logical Design for Data Modeling
ERD(Entity Relationship Diagram) is a specialized graphic that illustrates the interrelationships between entities in a database.
Data Dictionaryis a tool used to ensure the consistency of all elements in a system.
DFD(Data Flow Diagram) is a means of representing a system at any level of detail with a graphic network.
Physical Design for Data Modeling
IPO(Input Process Output) a chart that describes or documents the inputs to,the output from,and the functions performed by a program module.
HIPO(Hierarchy Input Process Output) a tool for planning and/or documenting a computer program that utilizes a hierarchy chart to graphically represents the programs control structure.
Wireframe is also known as a page schematic or screen blueprint, is a visualguide that represents the skeletal framework of a system.
Development Phases
SDLC using Waterfall Model. System Development Life Cycle. Defined by Raymond Mcleod in his book, System Development and Design, is a software development process, it is also a distinct process independent of software or other information technology considerations. It is used by a system analyst to develop an information system, including requirements validations, and user ownership through investigation, analysis, design, implementation and maintenance.
Implementation Phases
- Unit Testingis a method by which individual units of sourcecode are tested to determine if they are fit for use. A unit is the smallest testable part of an application.
- Link Testing testing of a group of modules to ensure that the modules operate correctly in combination. It is normally performed after the individual modules have been tested in isolation and prior to the integration testing that is performed for the complete system.
- System Testing the process of performing a variety of tests on a system to explore functionality or to identify problems. System testings’ usually required before and after a system is putin place.
- User Testing the user test is the most effective method for evaluating usability. It allows todirectly observe the user when he is using the application. User testing provides a means to identify the usability problems in real terms. Usability could be measured during the test by calculating the user performance.
- Pilot Testing is a trial run of procedures and instruments that you plan to use.
Evaluation Phases
Analysis of the result. The method used in analyzing the result of the survey is the lickert scale method. The researchers used this method to evaluate the performances of the objective of the study.
Locale of the Study
The proposed system entitled “Computerized Student Information System for ISU-E Laboratory High School” is generic in nature; they could be used by the students of the ISU laboratory high school, for the purpose of data gathering, testing and implementing the proposed student information system, the researchers had chosen the Isabela State University laboratory high school in San Fabian Echague, Isabela through investigation, the proposed system was evaluated, tested and implemented in the said agency and likewise to validate he efficiency and effectiveness of the system.
Respondents of the Study
The respondents of the study are the principal, secretary, teachers, and students of the ISU-E Laboratory High School, and also the IT professionals. The respondents are responsible in evaluating the student information system in terms of its reliability, portability, usability, userfriendliness, efficiency, and error-handling capabilities. They were chosen as the respondents in charge for evaluating the computerized student information system for ISU-E Laboratory High School in order to meet the objectives of the study.
| Description | Number of Respondents | Percentage |
| Teacher/Staff | 5 | 10% |
| IT Professionals | 10 | 20% |
| Non IT Professionals | 10 | 20% |
| IT Students | 15 | 30% |
| Non IT Students | 10 | 20% |
| Total | 50 | 100% |
Table 1.3 Breakdowns of the Respondents
Software Product
Hierarchical Input Process Output
The Hierarchical Input Process Output (HIPO) is a tool for planning and/or documenting a computer program that utilizes a hierarchy chart to graphically present the program’s control structure and asset of IPO charts to describe the inputs to the outputs from, and the functions performed by each module on the hierarchy chart.
The HIPO tool was used to present the logical structure of the proposed Computerized Student Information System for ISU-E Laboratory High School which was designed and developed based on its presentation.
Entity Relationship Diagram
ERD (Entity Relationship Diagram) It represents the logical flow of the system. The figure below contains different tables that contain relationship from each other’s.
Data Dictionary
The DD (Data Dictionary) is a tool used to ensure the consistency of all the elements in a system. It specifies such things as a standard field name or data item, whether the field will be alphabetic or numeric and the field width.
| Field Name | Length | Data Type | Template | Description |
| SN | 10 | Text | xxxxxxxxxx | Student Number |
| LN | 15 | Text | xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx | Last Name |
| FN | 15 | Text | xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx | First Name |
| M | 15 | Text | xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx | Middle Name |
| CA | 50 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxx |
Complete Address |
| BP | 30 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx |
Birth Place |
| BD | 10 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxx | Birth Date |
| Citizenship | 10 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxx | Citizenship |
| Gender | 1 | Text | X | Gender |
| CS | 10 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxx | Civil Status |
| Father Name | 30 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx |
Father Name |
| Father Occupation | 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxx |
Farther Occupation |
| Mother Name | 30 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx |
Mother Name |
| Mother Occupation | 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxx |
Mother Occupation |
| Parent Contact Number | 15 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxx |
Parent Contact Number |
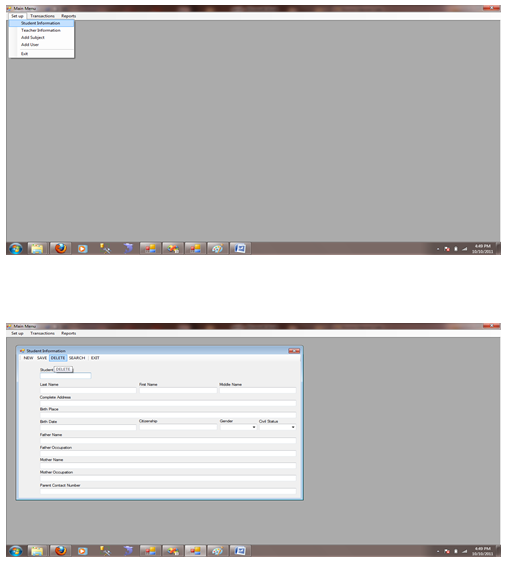
Figure 1.7.1 Student Information
| Field Name | Length | Data Type | Template | Description |
| TI | 10 | Text | xxxxxxxxxx | Teacher Id |
| TN | 30 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx |
Teacher Name |
| Address | 50 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Address |
| CN | 15 | Text | xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx | Contact Number |
| FOS | 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxx |
Field of Specialization |
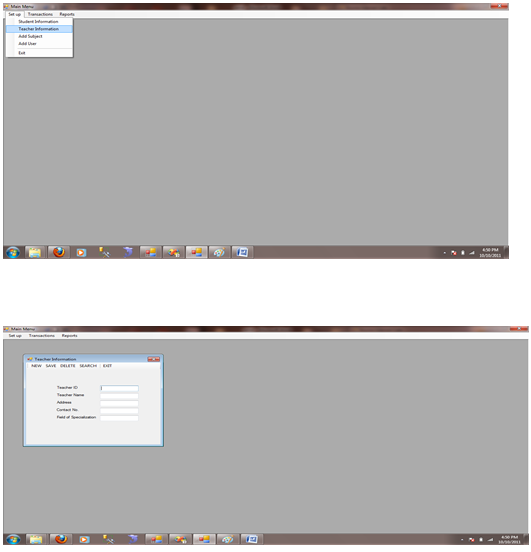
Figure 1.7.2 Teacher information
| Field Name | Length | Data Type | Template | Description |
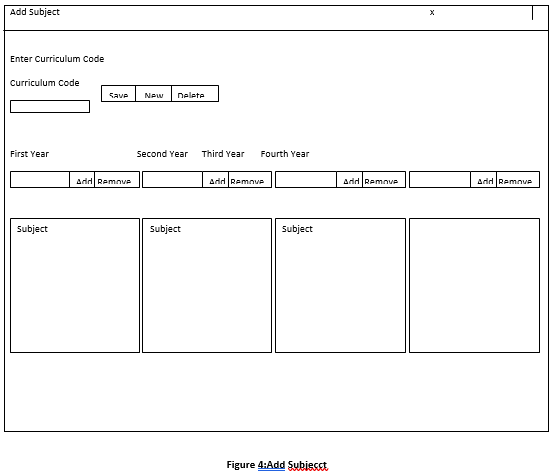
| CC | 10 | Text | xxxxxxxxxx | Curriculum Code |
| FY | 30 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx |
First Year |
| Subjects | 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subjects |
| 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subjects | |
| 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subjects | |
| 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subjects |
| SY | 30 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx |
Second Year |
| Subjects | 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subjects |
| 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subjects | |
| 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subjects | |
| 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subjects | |
| TY | 30 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx |
Third Year |
| Subjects | 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subjects |
| 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subjects | |
| 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subjects | |
| 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subject
s |
| FY | 30 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx |
Fourth Year |
| Subjects | 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subjects |
| 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxx |
Subjects | |
| 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subjects | |
| 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subjects |
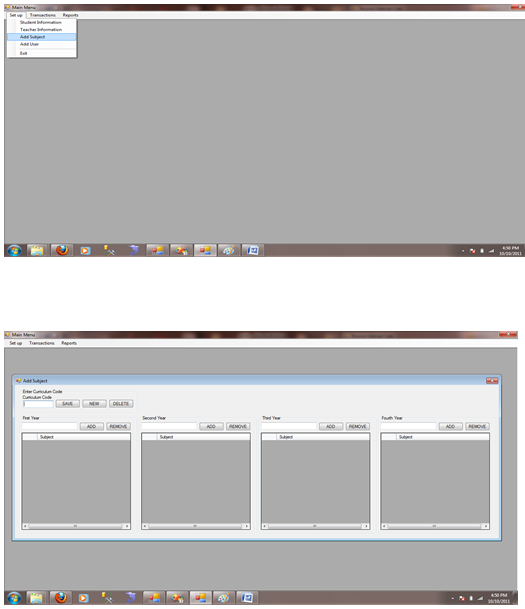
Figure 1.7.3 Add Subject
| Field Name | Length | Data Type | Template | Description |
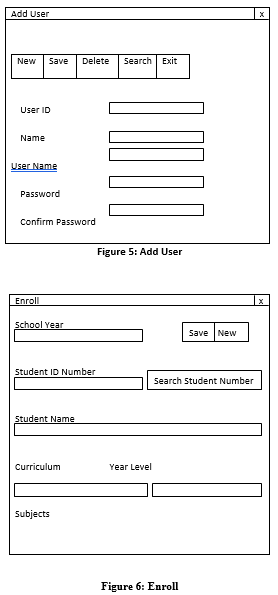
| UI | 10 | Text | xxxxxxxxxx | User ID |
| Name | 30 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx |
Name |
| UN | 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxx |
User Name |
| Password | 15 | Text | xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx | Password |
| CP | 15 | Text | xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx | Confirm Password |
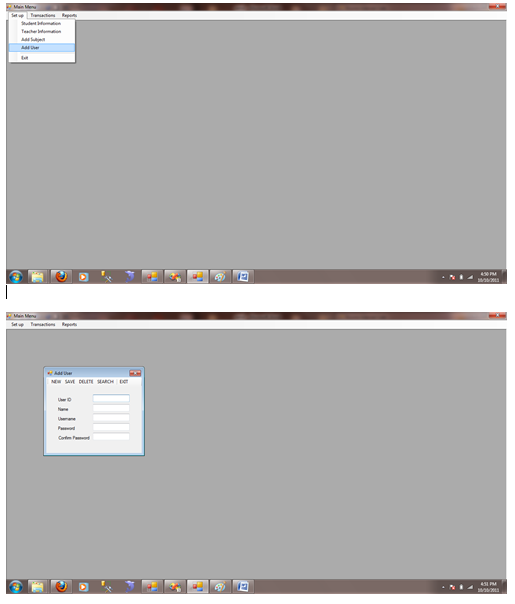
Figure 1.7.4 Add User
| Field Name | Length | Data Type | Template | Description |
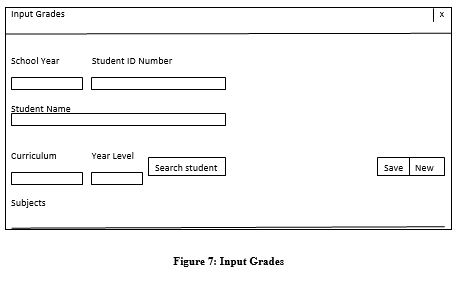
| SY | 10 | Text | xxxxxxxxxx | School Year |
| SI | 10 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxx | Student ID Number |
| SN | 30 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx |
Student name |
| Curriculum | 15 | Text | xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx | Curriculum |
| YL | 15 | Text | xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx | Year Level |
| Subjects | 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
xxxxx |
Subjects |
| 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subjects | |
| 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subjects | |
| 20 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxx |
Subjects |
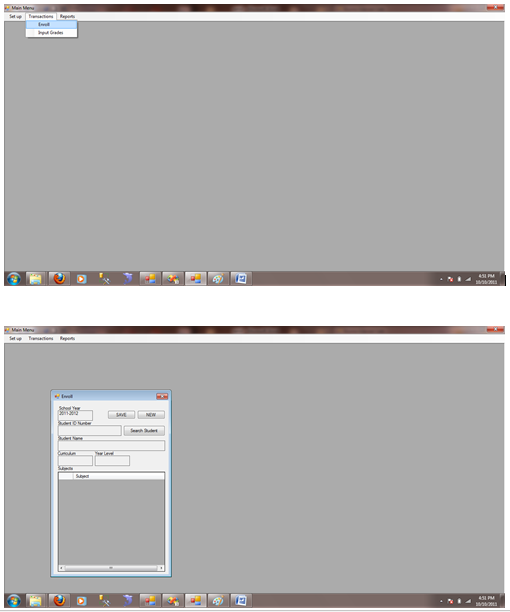
Figure 1.7.5 Enroll
| Field Name | Length | Data Type | Template | Description |
| SY | 10 | Text | xxxxxxxxxx | School Year |
| SI | 10 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxx | Student ID Number |
| SN | 30 | Text | Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx |
Student name |
| YL | 15 | Text | xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx | Year Level |
| 1st Grading | 2 | Text | xx | First Grading |
| 2nd Grading | 2 | Text | xx | Second Grading |
| 3rd Grading | 2 | Text | xx | Third Grading |
| 4th Grading | 2 | Text | xx | Fourth Grading |
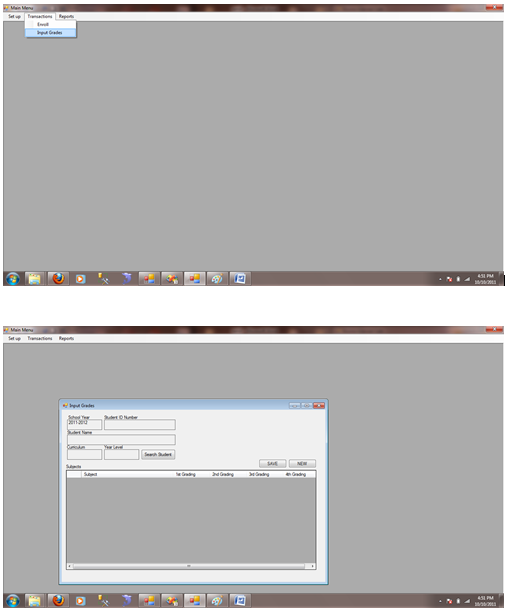
Figure 1.7.6 Input Grades
Cost and Benefits Analysis
The cost and benefit of the study talked about the development cost of the system, the operating cost of the existing system, the operating cost of the proposed system and the analysis of the system benefit. They are show in the succeeding tables.
Development Cost of the System
| Development Cost | Rate | Hours Requirement | Amount |
| A. Labor Cost | |||
| A.1. Analyst | |||
| Interviewing | 100 | 2 | 200.00 |
| Preparation of Report | 150 | 2 | 300.00 |
| Documentation | 250 | 3 | 750.00 |
| Contemplation | 250 | 3 | 750.00 |
| Preparation of Procedure | 250 | 1 | 250.00 |
| System Test | 250 | 2 | 500.00 |
| Inspection | 250 | 1 | 250.00 |
| Consolations (Programmers) | 300 | 3 | 600.00 |
| Forms Design | 250 | 2 | 500.00 |
| Formal Presentation | 250 | 2 | 500.00 |
| A.2. Programmer | |||
| Coding | 150 | 10 | 1500.00 |
| Document | 200 | 10 | 2000.00 |
| Customizing Program | 200 | 5 | 1000.00 |
| Consolation(Analyst) | 200 | 5 | 1000.00 |
| Formal Presentation | 150 | 5 | 750.00 |
| A.3. Operator | |||
| Conversion | 100 | 2 | 200.00 |
| Training | 100 | 3 | 300.00 |
| Program Support | 200 | 3 | 600.00 |
| Consolation(Analyst) | 100 | 4 | 400.00 |
| A.4. Management | |||
| Supervision | 75 | 4 | 300.00 |
| Consolation(Analyst) | 75 | 6 | 450.00 |
| Consolation(Analyst) | 150 | 5 | 750.00 |
| Formal Presentation | 150 | 5 | 750.00 |
| A.3.Operator | |||
| Conversion | 100 | 2 | 200.00 |
| Training | 100 | 3 | 300.00 |
| Program Support | 100 | 3 | 300.00 |
| Consolation(Analyst) | 100 | 4 | 400.00 |
| A.4.Management | |||
| Supervision | 75 | 4 | 400.00 |
| Consolation(Analyst) | 75 | 6 | 450.00 |
| A.5.Other | |||
| Data Entry | 75 | 4 | 300.00 |
| Art Form Design | 75 | 3 | 225.00 |
| Technical Writer (Document) | 75 | 3 | 225.00 |
| B.Equipment | |||
| B. 1.Existing Equip Test & Debug | |||
| Test & Debug Time | 75 | 1 | 75.00 |
| Other Supplies | 80 | 1 | 80.00 |
| B.2 Facilities Alteration | |||
| B.3.Installation Cost | |||
| Install Two(2) Circuits | 150 | 2 | 300.00 |
| C. Materials & Supplies (per month) | |||
| Papers, Form & Cards | 250 | 6 | 1500.00 |
| Presentation New Forms | 250 | 6 | 1500.00 |
| D.Overhead | |||
| Electricity | 4500.00 | ||
| TOTAL | 136.00 Hrs | 25,155.00 |
Figure 1.8 Cost and Benefit Analysis
Wireframe
Prototype
Hardware And Software Resources
Hardware Requirements
In implementing the computerized student information system, the following hardware specifications were required:
For the server–The systems run in Windows XP, processor at least dual core or higher, memory at least 1 GB DDR, 160 GB Hard disk space, 16” inches LCD monitor, video card at 512MB, keyboard, mouse, Avr , printer.
For the client– The systems run in Windows XP, processor at least dual core or higher, memory at least 1 GB DDR , 160GB hard disk space, 16” inches LCD monitor, keyboard, mouse, Avr, printer.
Software Requirements
The system is generic in nature. It will run on operating systems Windows XP or later version. It also run in Visual Studio 2008,MySQL 5.0 and SQL navicat. The software is also purposeful tool in generating such useful report as information.
Credits
Ramel P. Gasmin
Maricar C. Medina
Jonathan G. Lazaro





Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.