Barangay Health Management System Capstone Project Document
Introduction
In today’s information age, advancement of technology change the way of life. It has made various positive changes in almost every field whether it’s medical, business, education, sports or any field you look into. Particularly in most medical clinic facilities, it has made a big impact that enables modern clinics to serve many patients as possible (Qualman, 2018).
As the years passed, the number of patients has grown and various medical cases arise that the manual method of managing patients’ records and prescriptions were moved into computer-based systems.
Barangay Villamonte Health Center is using a manual system in terms of implementing medical services. To improve their services to the community, Barangay Health Management System is proposed to be implemented in the said barangay. It is designed for keeping and monitoring residents medical information in Barangay Villamonte. By this, paper works and manual record keeping will be minimize. Therefore, allowing the nurse and staffs to feel at ease in keeping track of patients and increasing the number of them served.
Background of the Study
Today, different means of record-keeping are used in health care settings. Some workplaces use hand-written records, others have moved to computer-based systems and many use a combination of both.
Barangay Villamonte Health Center is using a manual system in terms of implementing medical services, health programs, health monitoring and profiling. Their medical services and health programs include immunization, medical care, family planning and consultation. While health monitoring includes early childhood care and development and profiling of family profile. All these transactions are recorded manually. To improve the consistency of the consultation process of the said health center, Barangay Health Management System is proposed to be implemented in the said barangay.
The implementation of the Barangay Health Management System provides a quicker and more systematic way to record the medical information of the patients. It also provides reliable and secured personal medical records.
Every consultations or any transactions of the patients will be recorded or stored into a database including the monitoring and updating of the patient health records, how many patient accommodated daily, sickness or complaints report and the medicines released. It will simply increase the performance of medical personnel through its automated information system.
Statement of the Objective
Specifically, the study aims to:
- Design and develop a health management system for Barangay Villamonte that can:
- Allow only authorized user to access and record the medical records of the patients, they can also edit details if needed;
- Ability to easy navigate and manipulate the gathered medical records from the patients in the said barangay;
- Ability to monitor common sickness;
- Electronically record the inventory of medicines;
- View the schedule of their medical services;
- Generate comparative reports of illness in a month or a year to be submitted to the City Health Office (CHO).
- Evaluate the acceptability of the system using the adopted survey instrument based on ISO/IEC 9126 in terms of Effectiveness, Efficiency, Quality , Timeliness and Productivity.
Conceptual Framework
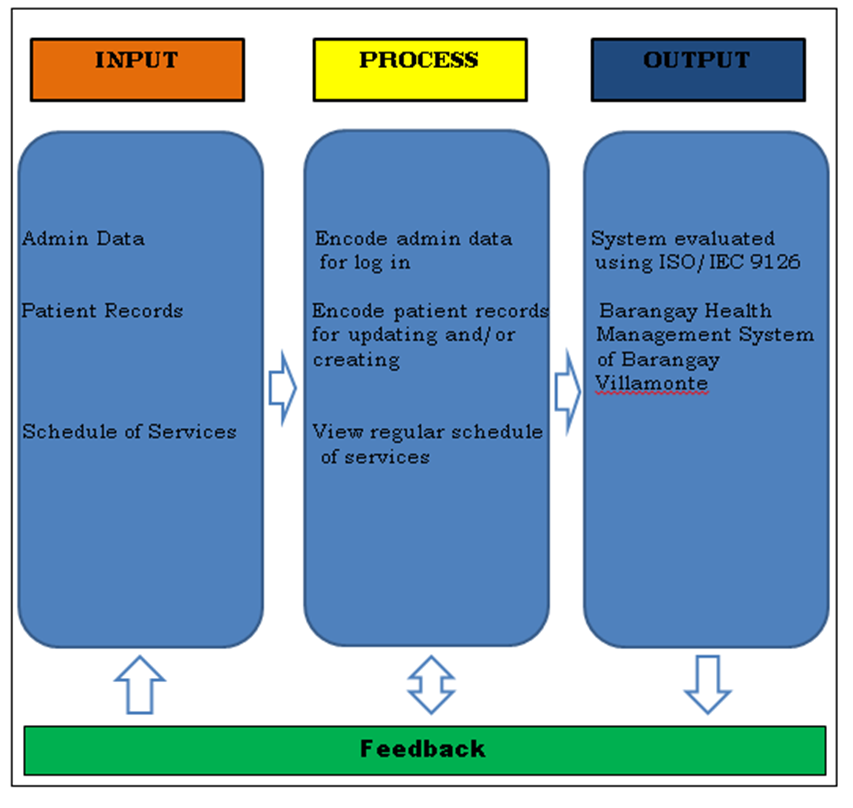
The conceptual framework shows and indicates the flow of the system and helps the users and all the readers understand how it will be processed. This study intends to improve the existing manual way of Barangay Villamonte Health Center. The Barangay Health Management System is an automated information system that is designed for keeping, and evaluating the residents’ heath records.
Figure 1 : Conceptual Framework of BHMS
Scope and Delimitation of the Study
In general, the focus of this study is directed towards the design and development of an automated health management system. This study is largely dependent on the information the barangay health secretary record and keep. This includes all the essential health records of all the residents of Barangay Villamonte.
Scope
The system is intended to the persons who have direct involvement in the processing of health programs and other medical services of Barangay Villamonte. The study dealt largely on the recording the Patient Profile Information of the Villamontehanon. The study involves the patients’ personal information such as their name, gender, birthdate, age, birthplace, status and occupation. While contact information includes their contact number, address (purok), guardian and many more. The medical history includes their weight, height, bloodtype, temperature, blood pressure, sickness and medicines received.
Every consultations or any transactions of the patients will be recorded or stored into a database including the updating of the patient health records, how many patient accommodated daily, sickness or complaints report and the medicines released.
Delimitation
In this proposed system, records and files are computerized and stored for accessibility and portability. However, the proponents limit the feature of the secure log-in system to the nurse and staff only. Web-access of the patients is not included.
Other services that the barangay is giving to its residents that requires information such in barangay health center is not part of the study. The proposed system can generate reports to the CHO.
Significance of the Study
The proposed Barangay Health Management System of Barangay Villamonte Heath Center, it will be beneficial for the following:
Barangay Health Worker. The staffs can benefit a lot from this study as they are integral part of the whole clinic management.
Clinic. The proposed system will automate every clinic tasks and can help maximize time spent with patients thereby providing better service to the community.
Nurse. The proposed system will make it easier for the head nurse to manage the clinic and it would be convenient when it comes to retrieving patient health records.
Patients. It will provide better service for the patients and their community.
Researchers. The researchers have developed their writing, analysis and skills in making a good thesis that can help in improving our community as a whole.
Future Researcher. This will benefit other researchers who wish to have similar studies. The results will serve as their background information in conducting their own research.
Definition of Terms
The definition of terms are based on concepts taken from the dictionary or web.
CHO. Conceptually, the term CHO is an acronym for City Health Office. It was created by virtue of Article 8 Title 5 Book 2 of the Local Government Code. Its mandate is to formulate and implement policies, plans, programs and projects to promote the health of the people in the city and to execute and enforce all laws, ordinances and regulations pertaining to public health.
Operationally,
Data. Conceptually, the term data is an information output by sensing device or organ that includes both useful and irrelevant or redundant information and must be processed to be meaningful. (Merriam-webster.com, 2017)
Operationally, it is a collected information that is processed and stored in a computer.
Database. Conceptually, the term database is a large collection of data organized especially for rapid search and retrieval as by a computer. (Merriam-webster.com, 2017)
Operationally, the proponents use the database to collect data and help make the Barangay Health Management System.
Inventory. Conceptually, the term inventory means to make a complete list of. (Merriam-webster.com, 2017)
Operationally, the term inventory means making a list of medicines available in the health center as well as other stocks.
Management. Conceptually, the term management is the process of dealing with or controlling things or people. (Merriam-webster.com, 2017)
Operationally, management is the process of controlling the inflow of day-to-day operations in the clinic, the programs as well as the schedules to be made.
Profiling. Conceptually, the term profiling is the act or process of extrapolating information about a person based on known traits or tendencies. (Merriam-webster.com, 2017)
Operationally, profiling is the process of filing medical informations about a resident in barangay Villamonte based on his/her medical history.
Recording. Conceptually, the term recording means setting down in writing or some other permanent form for later reference. (Merriam-webster.com, 2017)
Operationally, recording is having a chronological written account of a patient’s examination and treatment that includes the patient’s medical history and complaints, the physician’s physical findings, the results of diagnostic tests and procedures, and medications and therapeutic procedures.
Scheduling. Conceptually, the term scheduling means the arrangement or plan (an event) to take place at a particular time. (merriam-webster.com, 2017)
Operationally, the term scheduling is used to mean the time or schedule of consultation. It also determines when an activity should start or end depending on the duration.
Transaction. Conceptually, the term transaction is an exchange or interaction between people (Merriam-webster.com, 2017).
Operationally, transaction is the interaction between health staffs and patients. How many patient accommodated daily, sickness or complaints report and the medicines released.
Villamontehanon. Operationally, the term Villamontehanon refers to people living in Barangay Villamonte.
Review Of Related Literature
This chapter discusses the existing study into the context of proceeding related research. This research study cited articles and systems related to the research topic.
Local Studies
Barangay Management Information System for Cities and Municipalities in the Philippines
The Barangay Management Information System for Cities and Municipalities in the Philippines is a program which contains features that records and manages information and at the same time can send documents from barangay hall to the city hall. Barangay Management Information System for San Carlos City is an online and offline system to keep, process, retrieve and update Barangay and City Hall information through a secure network interface. It is designed to handle a wide-range of information relating to barangay profile, constituents profile, barangay clearances, barangay disputes/cases, barangay activities, and barangay legislation and City Hall’s required reports from the barangay. It covers all the functions, activities and transactions of the barangay which aims to provide complete and accurate information for the barangay and city hall management and stakeholders. The study was the solution to the problems stated and to enhance the quality of service a barangay office offers to its clients (Soriano et. al, 2018).
Computer-based information operates through the use of software that can offer information services for an institution or organization. It is powerful and convenient builder for simultaneous growth in society and industries. An information service provides a way to electronically access, retrieve, and transmit that information.
Furthermore, this serves as an awakening factor for all government offices, from highest to lowest levels, to be in line with the government’s view of globalization and competitiveness in today’s information age. (Henczel, n.d.)
Barangay Health Center Information System
The implementation of the Barangay Health Center Information System simply improves the consistency of the consultation process of the Barangay Dian-ay Health Center. It is very useful to both the Barangay Health Center and to the patients. To monitor all the Patients health records is very necessary. Through this system it provides satisfaction & better service to the beneficiary/community it is serving.
It will increase the performance of medical personnel through its system generated consultation. To help the health center of Barangay Dian-ay continually do their mission, vision, and goals through providing their services fully hearted to the Patient/Community of the Barangay Dian-ay for the medication/treatments. (Allura, n.d.)
Foreign Related Studies
Integrated System Health Management
A sensor system and its optimal deployment, selection and information fusion are the basic research areas of ISHM. Schmalzel proposed a smart sensor-based health management system architecture. Nickson developed a networked intelligent wireless sensor for engine health management. Bonissone proposed a framework for computational intelligence in ISHM, which defines the time horizons for ISHM decision-making across products and the type and structure of domain knowledge. NASA has conducted a number of institutions on aircraft engine health management to develop data-mining methods for aircraft engine health management and enhanced self-tuning airborne real-time models to enable adaptive hybrid data and information fusion applications.
An important part of integrated system health management (ISHM) is performance assessment, which is conducted at all important space exploration system stages; development, stereotypes, production, and equipment. Spacecraft system design has a long development cycle, generally goes through several phases such as the identification of technical indicators, conceptual design, detailed design, prototype construction, validation tests and flight tests and encompasses considerations such as costs and risk assessments. Therefore, accurate and reliable performance assessment drives design adjustments and predicts maintenance requirements and early fault diagnostics and prognostics. As launch success rate assessments are considered the most important space exploration system performance evaluations, using lunar exploration as an example, this chapter proposes enhanced launch success ratio assessment models to illustrate ISHM performance evaluations. (Figueroa et. al, 2006).
Related Systems
Synthesis
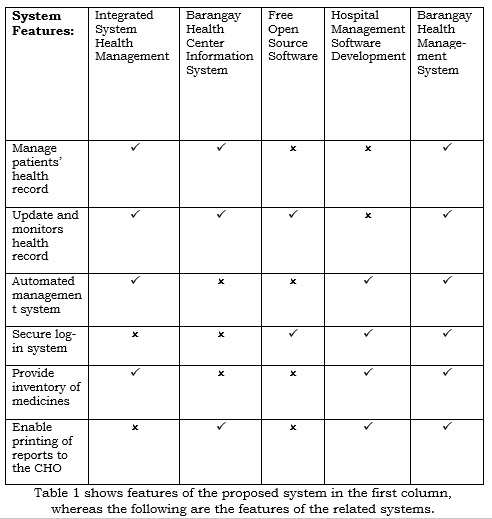
The system presented were obtained from both foreign and local system study that were made basis for the developed of health management system. It describes some features that are available on the system but some are not available with the local and foreign study.
According to the journal entitled, Reducing the frequency of errors in medicine using information technology; appropriate use of information technology in health care resulting in process simplification could result in substantial improvement in patient safety. The growing demand for the quality healthcare should carry out planning, monitoring and controlling the delivery system. This characteristics are the main features of the Barangay Health Management System.
Thus, the related system shares similar nature to the study but the proponents observed the lack of features which are important such as management of patients’ health records; automated management system; secure log-in system; inventory of medicines; generate the monthly reports to the CHO. Hence, the proposed system includes all the needed features specifically tailored for Barangay Villamonte Health Center.
Methodology
This chapter discusses the research strategy and procedures on how the system flows and its phases.
Software Development Life Cycle
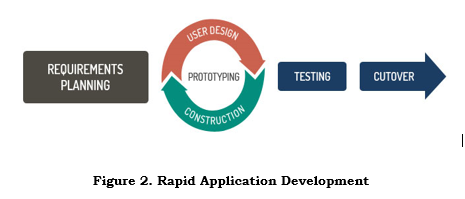
Tatva (2013) states that Rapid Application Development (RAD) is an effective methodology to provide much quicker development and higher-quality results than those achieved with the other software development methodologies. It is designed in such a way that, it easily takes the maximum advantages of the software development. The main objective of this methodology is to accelerate the entire software development process. The goal is easily achievable because it allows active user participation in the development process. The Rapid Application Development Model is broken down into different phase. Basic phases of Rapid Application Development are as follows: Requirement Planning, Prototyping (user design and construction), Testing and Cutover.
Requirements Planning
During this initial stage, after we selected our team members. The Researchers assigned tasks and assignments to each other. After the researchers did their brainstorming about the title of the system, they did the interviews and surveys to the Barangay Health Worker (BHW) of Villamonte. Here, they also sought for some related studies of the system.
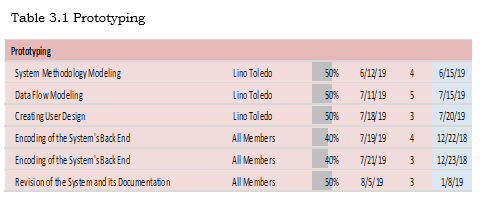
Prototyping
In this phase, the researchers selected Rapid Application Model as the best methodology that would fit best for the system and the team. Also, in this phase, modeling was created to give a better view for the researchers for the overall scope of the system and its processes. After,
the prototype was created to give the programmer the design of the system. Then, the coding started.
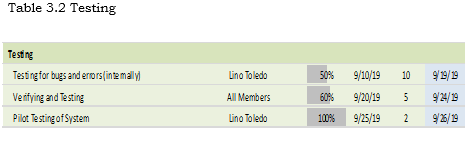
Testing
Proponents have conducted a testing survey where 30 respondents from the Health Center and their staffs evaluated the system using the User Acceptance Survey. To see whether it functions and operates just how they want it.
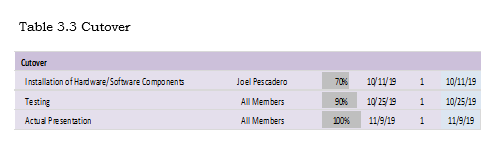
Cutover
Results the final tasks in the SDLC implementation phase, where the system was concluded to function well. In this phase, the system was again presented and trainings were made for the staffs of the company. It will all be up to the City Health Officer if she would want to use the system for their health center.
Operational Feasibility
Front End
Bootstrap is an open source toolkit for developing with HTML, CsS and Js. Quickly prototype your ideas or build your entire app with Sass variables and mixins, responsive grade system, extensive prebuilt components, and powerful plugins built onXx x Jquery. (Wama Software, n.d)
Back End
PHP
PHP is a server-side scripting language desined for web development but also used as a general-porpose programming language. Originally created by Rusmus Lerdrof in 1994, the PHP reference implementation is now produced by the PHP group (Wikipedia, n.d.)
Technical Feasibility
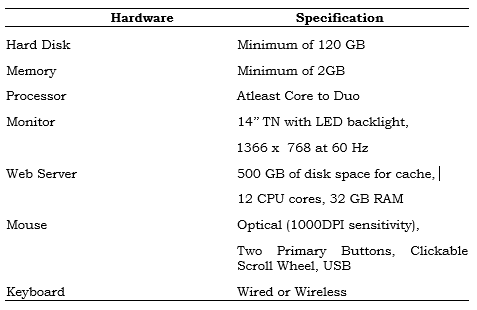
Hardware Requirements Specification
The Barangay Health Management System has the appropriate hardware that is suitable in following maximum and recommended hardware services helpful to the development of the system study.
Table 2.0 Hardware Specification
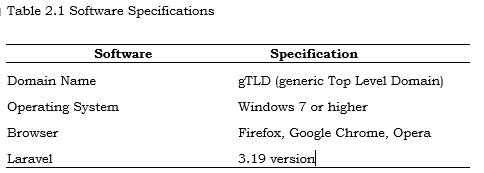
Software Requirements Specifications
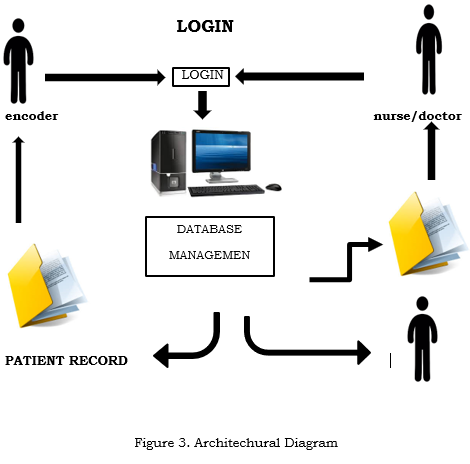
System Architecture
Figure 3.0 illustrate how the system will flow. The patients go to the health center in a scheduled time based on the center’s scheduling. The BHW then ask the patient about his/her personal information as well as their medical history. All these facts are encoded by a BHW. After they have assisted their patients, they will go see the doctor.
Feasibility Schedule
The feasibility schedule contains the record of the amount of time the proponents spent on the system.
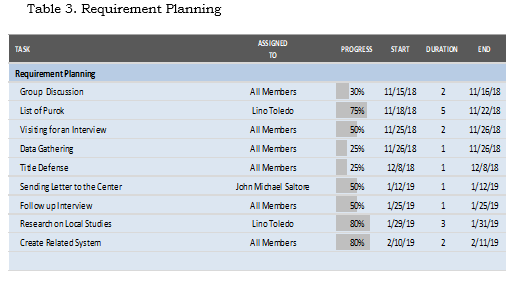
Gantt Chart
The following tables show the Gantt chart of the tasks that have been done by the proponents with the time allotted for the establishment of the entire system.
Table 3. Requirement Planning
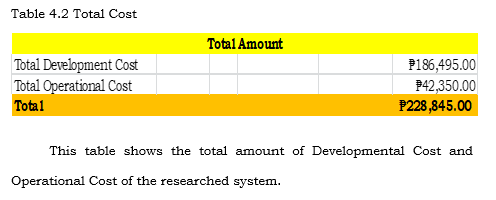
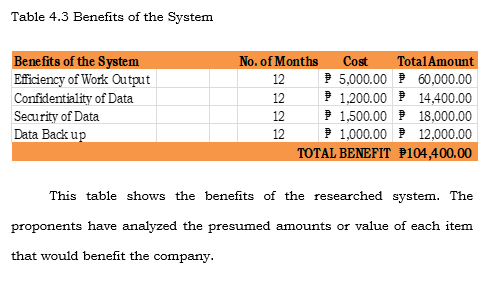
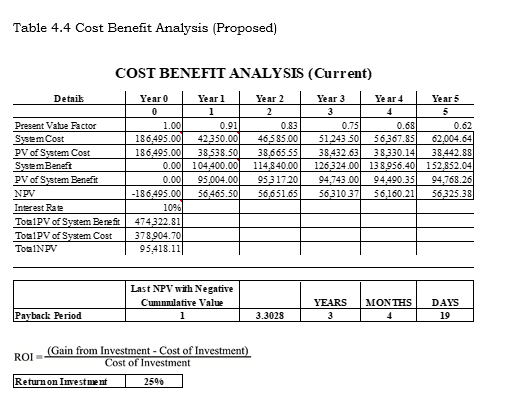
Cost Benefit Analysis
Cost Benefit Analysis or the CBA is a process wherein business decisions are analyzed. The benefits of a business-related action are summed and the costs associated with taking that action are subtracted to determine whether the company can benefit from the system.
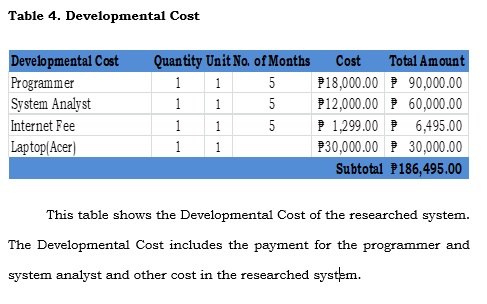
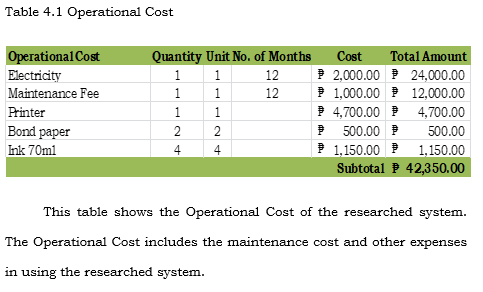
Table 4.4, shows a chart of the Cost and Benefits Analysis. The Return of Investment comes out of 25%. The Payback Period was computed by taking the sum of the Present Value of System Benefit (Php 95,004.00) subtracting it to the Present Value of System Cost (Php186,495.00) to get its Net Present Value and get the sum of Net Present Value (Php 56,465.50) subtracting it to the negative value of System Cost (Php -474,332.81), and dividing the difference Net Present Value (Php 56,465.50). Resulting to 1.64 which is round to 2, making it a 2-year payback period. Payback period Initial Investment/Cash Inflow. The ROI was computed by taking the sum of the Total Present Vahie of System Benefits (Php 474,332.81), subtracting it to the Total Present Value of System Cost (Php 497,185.08), and dividing the difference Total Present Value of System Cost (Php 378,904.70). The quotient is is equivalent to 25% of ROI or Return of Investment. The formula that the proponents used can be seen on Table 4.4.
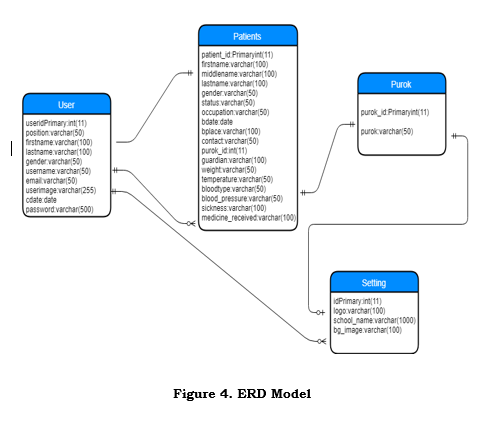
ERD Model
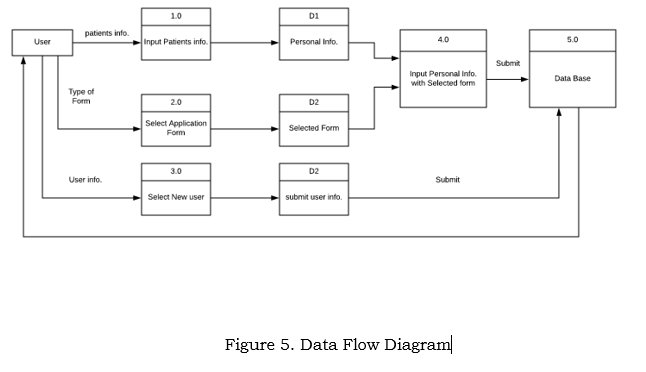
Data Flow Diagram
The flow of the system begins when the user process daily check up. After the all data will be converted into information and stored inside data base, and then data inside the database can be accessed by the admin.
Data Dictionary
Table 5. Patient
Table 5 shows the patient’s information composes of Id, Fname, Mname,, Lnam, Gender, Status, Occupation, Bdate, Bplace, ContactPurok_id, Guardia, WeightTemperature, Blood Type, Blood pressure, Sickness, Medicine received
| Field name | Data Type | Length | Key | Description |
| Id
Fname Mname Lname Gender Status Occupation Bdate Bplace Contact Purok_id Guardian Weight Temperature Blood Type Blood_pressure Sickness Medicine_recieved |
Int
Varchar Varchar Varchar Varchar Varchar Varchar date Varchar Varchar int Varchar Varchar Varchar Varchar Varchar Varchar Varchar |
11
100 100 100 50 50 50 100 50 100 50 50 50 50 100 100 |
Primary Key
FK |
Primary
Family name Middle name Last name Gender Status Occupation Birth place Contact Purok_id Guardian Weight Temperature Blood type Blood pressure Sickness Medicinere cieved |
Table 5.1 Purok
Table 5.1 shows the details of purok.
| Field name | Data Type | Length | Key | Description |
| Purok_id
purok |
Int
50 |
11 | Primary Key | Primary key
purok |
Table 5.2 Setting
Table 5.2 shows the details of setting.
| Field name | Data Type | Length | Key | Description |
| Id
Logo School_name Bg_image |
Int
Varchar Varchar varchar |
11
100 1000 100 |
Primary Key | Primary key
Logo School name background name |
Table 5.3 User
Table 5.3 shows the table of user pomposes of User_id, Position, Fname, Lname, Gender, Username, Email, Userimage, Cdate, password.
| Field name | Data Type | Length | Key | Description |
| User_id
Position Fname Lname Gender Username Userimage Cdate password |
Int
Varchar Varchar Varchar Varchar Varchar Varchar Varchar date Varchar |
11
50 100 100 50 50 50 255 500 |
Primary Key | Primary key
Position Family name Last name Gender Username Userimage Password |
Presentation, Analysis, and Presentation of Data
This chapter exhibits the results of the User’s Survey conducted for the system to the Barangay Health Worker and Villamontehanon.
Presentation
The proponents demonstrate the system’s functionality to the randomly selected respondents. The proponents observed the respondents on how they response to the system. The respondents were evaluated using the User Acceptance Survey in order for the them to distinguish the level of acceptability of the proposed system.
Data Analysis
To interpret the results of the survey, the researchers utilized a statistical tool to provide meaningful data for the survey conducted. According to Bettany-Saltikov & Whittaker (2014), it is important to select a statistical test which can answer the researcher’s objectives of the study and the field of research.
This section presents the analysis of the data collected and gathered from the respondents: Barangay Health Workers, Villamontehanon, Barangay Kagawad and Barangay Staffs.
Characteristics of the Respondents
Table 6. Frequency of Respondents
Respondents Frequency
City Health Officer 1
Barangay Health Workers 6
Villamontehanon 15
Barangay Kagawad 1
SK Chairman 1
Barangay Staffs 6
Total 30
The population is composed of the City Health Officer, Barangay Health Workers, Villamontehanon, Barangay Kagawad and Barangay Staffs. The proponents got thirty respondents from the administration and Barangay staffs.
Table 6. shows the number of respondents who have answered the User-Acceptability Survey. The researchers got a total number of 30 respondents.
Participants of the Study
The population of the study was determined using purposive sampling with 30 identified participants intended for the system which is comprised of a City Health Officer, Barangay Health Workers, Villamontehanon, Barangay Kagawad and Barangay Staffs. This was supported by Edralin (2002) which states that “selection of key informants is based on predetermined set of criteria”.
Interpretation of Data
Table 6.1 Verbal Interpretation
Mean Score Range Verbal Interpretation
4.21-5.00 Very Satisfied
3.41-4.20 Satisfied
2.61-3.40 Dissatisfied
1.81-2.60 Very Dissatisfied
1.00-1.80 Poor
The evaluation of the system was conducted using the adopted survey instrument based on ISO/IEC 9126 in terms of five (5) categories namely: Effectiveness, Efficiency, Quality, Timeliness and Productivity.
The items of the evaluation instrument were appropriate for field testing situation. The first category was composed of four (4) items, the second category was composed of three (3) items, and the third, fourth and last categories were composed of four (4) items. Table 6.6 shows that the user’s survey result for the system’s quality came back with a total mean of __which interpret that the users were very satisfied with the system’s quality after testing it.
Effectiveness
Table 6.2 Survey Result – Effectiveness
System Quality Performance Total Mean Verbal Interpretation
Effectiveness 4.65 Very Satisfied
Table 6.2 shows that the user’s survey result for the effectiveness of the system came back with a total mean of 4.65 which is interpret as “Very Satisfied” which means that the end-users were satisfied with the system’s effectiveness after testing it.
The respondents stated that the proposed system (BHMS) meet the desired result and produces the desired output. They also stated that the system is effective, it means that the level of functionality of the developed Information System is high.
Efficiency
Table 6.3 Survey Result – Efficiency
System Quality Performance Total Mean Verbal Interpretation
Effeciency 4.67 Very Satisfied
Table 6.3 shows that the users survey result for the system’s efficiency came back with a total mean of 4.67 which interpret that the users were very satisfied with the efficiency of the system after testing it.
The respondents stated that the system (BHMS), has the ability to avoid wasting materials, energy, efforts, and time in generating and recording statistical reports. In a more general sense, the system (BHMS) has the ability to do things well, successfully and can be easily performed.
Quality
Table 6.4 Survey Result – Quality
System Quality Performance Total Mean Verbal Interpretation
Quality 4.65 Very Satisfied
Table 6.4 shows that the user’s survey result for the system’s quality came back with a total mean of 4.65 which interpret that the users were very satisfied with the system’s quality after testing it.
The respondents stated that the system (BHMS), meet the standards of the users in terms of its degree of excellence.
Timeliness
Table 6.5 Survey Result – Timeliness
System Quality Performance Total Mean Verbal Interpretation
Timeliness 4.67 Very Satisfied
Table 6.5 shows that the user’s survey result for the system’s quality came back with a total mean of 4.67 which interpret that the users were very satisfied with the system’s quality after testing it.
The respondents stated that the system (BHMS), has the quality in generating and recording statistical reports in favorable or useful time. Furthermore, Nelson, Todd and Wixom (2005) added that the accuracy of the information and being up-to-date most of the time is vital for a system.
Productivity
Table 6.6 Survey Result – Productivity
System Quality Performance Total Mean Verbal Interpretation
Productivity 4.76 Very Satisfied
Table 6.6 shows that the user’s survey result for the system’s quality came back with a total mean of 4.76 which interpret that the users were very satisfied with the system’s quality after testing it.
The respondents stated that the system (BHMS) has the ability to produce a desired result. It also implies that the users are able to find the system as simple to use which led them to have better efficiency and speed in accomplishing their tasks as compared to their previous process without the system.
Over All
Table 6.7 Survey Result – Over All
System Quality Performance Total Mean Verbal Interpretation
Over All 4.68 Very Satisfied
Referring now to the overall impression of the users toward the Barangay Health Management System as shown in table 6.7, it obtained a “Very Satisfied” level of satisfaction with a mean of 4.68.
This implies that the system is functional and addresses the objectives of this study with high approval towards its users. It is also evident that the users were satisfied with the system, simply means that their existing system of record-keeping had difficulties and was successfully addressed by BHMS. Furthermore, this would also mean that the system made the users felt comfortable by utilizing the system due to its simplicity but at the same time making them more productive.
Summary Of Findings, Conclusion And Recommendation
This chapter presents the summary of the findings, and the conclusions and the recommendations for the system study.
Summary of Findings
The result of the evaluation of the system arrived at the following findings:
- The Overall Satisfaction (overall) of the Barangay Health Management System which was taken from the average responses of the different categories from the survey instrument was “4.68” interpreted as “Very Satisfied”.
- The system Effectiveness which was taken from the average responses of first category from the survey instrument was “4.65” interpreted as “Very Satisfied”.
- The system Efficiency which was taken from the average responses of first category from the survey instrument was “4.67” interpreted as “Very Satisfied”.
- The system Quality which was taken from the average responses of first category from the survey instrument was “4.65” interpreted as “Very Satisfied”.
- The system Timeliness which was taken from the average responses of first category from the survey instrument was “4.67” interpreted as “Very Satisfied”.
- The system Productivity which was taken from the average responses of first category from the survey instrument was “4.76” interpreted as “Very Satisfied”.
Conclusion
The system got an overall result of “4.68” which indicates that the users “Very Satisfied” with the usefulness of the Barangay Health Management System. This means that the system meets the objectives of the study. It also indicates that the system is able to provide the barangay health center a system that performed accordingly to its functions and purpose. In other words it has addressed the necessary automation requirement of the center after the thorough system study.
Recommendations
Based on the findings and conclusions of the study, the following recommendations were given:
- The system would be best implemented in the health centers of every barangay in Bacolod City.
- Add more features such as communication of the Barangay Health Workers (BHW)and patients.
- Add more features where in patients can be updated during their scheduled consultation and others.
- The system must have maintenance for every six (6) months to maintain and update its functions and also for security of its databases.
- Further research is encouraged to extend the applicability of the system to other areas.
Credits
Pescadero, Joel A.
Saltore, Jhon Michael
Toledo, Lino S.




Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.