Barangay Services Management System Capstone Project Document
Introduction
Nowadays where the computer and the technology is very critical and online communication is part of living, the people who are using it all over the world are different. Most of the barangay that we worked with paper but they all know that day by day the population of their barangay is increasing. In the past, it was easy to use paper because there were fewer residents and it was easier to manage them.
In the past years, there were only few resident in the barangay Mandalagan, so that could be easily managed the paper works of all the resident. But as the years went by, the population of barangay Mandalagan got bigger and the barangay couldn’t handle all the request of the residents and this made it difficult to manage because of that bigger population. The resident would always wait for the duty officer who was in charge for that day, then they would form a line to take care of their needs.
With the help of technology, barangay duty officer can make and keep records, announcements, reports, reservations such that the residents can have records and access to them.
In this study, we want to allow barangays Mandalagan of Bacolod City the ability to avoid paperwork and computer services so that they can serve their residents more easily.
Background of the study
Barangay Mandalagan is one of the oldest Barangays in the City of Bacolod. It formally became a chartered barangay by virtue of the republic act 2730 (Revised Barrio Charter 3590).
Presently Barangay Mandalagan has thirty-six (36) puroks and 29 Major Subdivisions. It is one of the biggest Barangay in terms of population density with more or less 27,000 people in households. It has a voting Strength of about 12,500 registered voters (more or less).
The proponents design and develop a management system, where the residents view the announcements, blotter, get reservations and other important matters. Also, the Officials can keep the records of the residence and report it.
Statement of the Objective
This software system can announce the events of the Barangay, give reports and records files.
- Cater to the residents request for service from the Barangay such as creation of foot walks, installation of street lights, drainage cleaning, and so on.
- Provide information of the Barangay as well as provide announments about events in the Barangay.
- Provide clearances or permits in the system and allow the residents to go online to fill out requisite forms.
- Evaluate the acceptability of the system using the adopted survey instrument base on ISO/IEC 25010 in terms of effectiveness, efficiency, quality, timeliness and productivity.
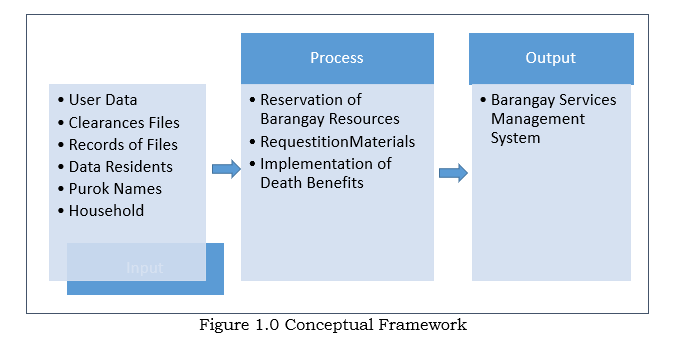
Conceptual Framework
The Barangay Services Management System is a system that can be accessed by multiple users. The user is allowed to register, learn of the schedule of events, gain access to allowable demographic info, and make reservation. It allows any authorized person to view all the personal data and the requests of the barangay residents in the system. It will guide the first user in how to access the system.
Scope and Limitation of the Study
This section enumerates the scope covered by the study and its delimitation.
Scope
Our scope is to access all residents of Barangay Mandalagan that they can easily request, receive clearances and permits from the Barangay Mandalagan Officers. The residents can use this system using their cellphones, computers and tablets to access their needs. The residents can easily know the details, information, announcements, available services and other services that the barangay can accommodate the needs of the residents. The registered residents will be aware for every announcement of the Barangay Mandalagan. The system will also display the schedule of activities of the Barangay Mandalagan. Also the system gives print records and clearances. Through this system, it will simply the terms of record keeping. This system is only available to the Barangay Mandalagan.
Delimitation
The system is designed for the Barangay Mandalagan, it doesn’t cover the personal costs for different payment of bills of residents. For instance, the cost of utility bill to the resident is not cover. The system does not cover third-party announcements like job fairs and access to online services is not available. The systems are not also for the renters or tenants of the Barangay Mandalagan or any workers of all the tenants of the Barangay. The pay bills are not connected to this system or others transaction that related to accounting process.
Significance of the Study
Barangay Captain- can check easily all of the information and records of his/her barangay residences.
Secretary– can help to facilitate barangay work and to provide more services to all residents.
Residence– the primary advantage of the BSMS is time savings. The resident will only make one trip to the barangay officers to make final payments and pickup of their online request document.
-can easily request to the barangay Secretary via the internet and they can get their immediate certificates and services without incurring public transportation costs. They can fill out their own Barangay Clearances as well as other forms or needed documents.
Researcher– will learn which documentation requirements are necessary from the local government agency (barangay Mandalagan).
Future Researcher– can get an idea and find related studies and compare it to their own work.
Definition of Terms
Administrator. checks the proposed system and the work of the students who are conducting the research. The admin will be the one to check the individual group or individual student’s work.
Operational, a person responsible for running a business, organization, etc.
System. the set of details and information that works together to perform a function.
Operational, is a type of computer program that is designed to run a computer’s hardware and application programs.
Database. stored data of resident information, user, events announcement, puroks, purok officials, names of officials.
Operational, a database is a collection of information that is organized so that it can be easily accessed, managed and updated. Computer databases typically contain aggregations of data records or files, containing information about sales transactions or interactions with specific customers.
Management. a group of details that holds all of the information of a company.
Operational, the process of dealing with or controlling things or people.
BSMS– The acronym of Barangay Services Management Systems
Review Of Related Literature
Related literature is the review of the local and foreign studies and how they compare to our work. Some studies have a difference from the others.
Barangay Management Information System
Barangay Management Information System with SMS (Short Message Services) support. This provides a record keeping and updating information and it also allows the users to search or view records. It is for the benefit of a Barangay but this time this proposed system is with SMS Support. SMS Support needs a broad band connection to send messages to the constituents. The SMS support can’t accommodate to send to all the residents of the Barangay. Computer-based information retrieval operates through the use of software that can offer information services for an institution (Kazuya,2015.
Barangay Management System (BMS)
This system facilitates barangay management by enabling the client barangay to maintain their resident records as complete up to date as possible and as easily accessible for verification’ monitoring and reference. It consists of Automatic Business Process which facilitates processing of Barangay Clearances and others such as charges which are sources of Barangay revenues. It also allows other Barangay related functions such as blotter reports and other related services. Forms and Reports that prepares and prints Barangay Permits and Certifications. Standard based conforms with Local Government Code Sec. 394 which provides that each barangay maintains updated record of residents for easy identification of updated reference on the Local Barangay Statistics (Mirasol, 2015).
Computerized Information System
The purpose of this study is to maintain complete and up to date which is easily accessible for verification’ monitoring and reference purposes. Also they can automate record keeping process in order to produce efficient and accurate report and proper automated file management. The system assurance that the file will be protected and safe for and it also require authorization before someone can access the system. This will ensure that the file will securely store in the system and makes back-up data of the file if technical accidents occurs. It can also generate report to the municipality about the status of the Barangay. The propose will have a significant effect on both residents of the Barangay and Barangay employees who manages the system as well as the Barangay itself. Their implementation is to change the method and process that the Barangay accustomed in keeping their files. This will also ensure that all the records will be intact and updated (Lado, Maloloy-on, Perez, Rizaldo, Tacocong, 2017).
Foreign Related Studies
Concurrency Management System Florida
The Bay Country Concurrency Management System contains Adopted Level of Services Standards and Maximum Services Volumes for Country and State Road Segments monitored by the Country. They also reserve trips on daily basis which in turn may affect the level of service of the roadway segments. The Communications Office is responsible for producing a variety of publications’ maintaining media relations and supervising other special projects. They also aim to enhance the community’s access to Bay Country. This one-person officer is responsible for maintaining positive community and media relations. The Community Director also heads dissemination of information to the public’ news media and other governmental entities. The Board of County Commissioners offers a wide variety of jobs’ excellence benefits and opportunities for advancement.
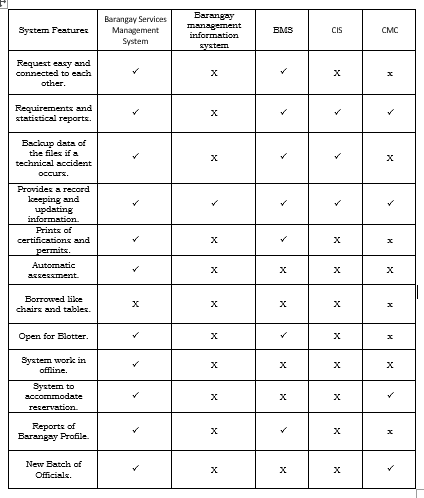
Related System
Table 1: Related Systems of BSMS
Table 1 shows features of the proposed system in the first column, whereas the following columns are the features of the related systems.
Synthesis
The system that was presented was based on both foreign and local system studies that were made of their information systems. It has also described the features that are available on the system that are not available from the other systems.
All the related systems represented have similar essential features to the study but it was observed that most of their systems had a lack of Automatic Assessment. Automatic Assessment allows residents request for permits and clearances to be digitally reported and recorded, such permits, documents request would be available in a timelier fashion when the resident arrived at the barangay officer to pay and pick up their documents. It was observed that all barangays are providing record keeping and updating information. Also, one thing we observed was the lack of available printing for certifications and permits.
The system discussed are correlated to the proponents’ system, the Barangay Services Management System of Mandalagan, Bacolod City. The researchers analyzed accurately and evaluated the related system based on its modules and its functions, saw its problems and added greater functionality than those other system.
Methodology
This chapter present the flow of system and system analysis and development employed in this study. Each of the utilize approaches are explained based on it use and on the process of developing the system.
System Development Life Cycle was to build on one another, framework defining task performed at each steps in the software development process.
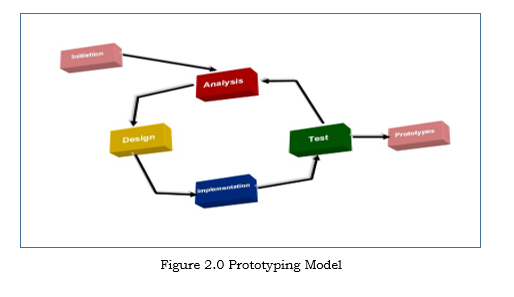
The prototyping model is a systems development method in which a prototype is built, tested and then reworked as necessary until an acceptable outcome is achieved from which the complete system or product can be developed. This model works best in scenarios where not all of the project requirements are known in detail ahead of time. It is an iterative, trial-and-error process that takes place between the developers and the users (Rouse,2005).
Development process refers to structures of development of software. It describes the variety of task of development software processes as Initiation, Analysis, Design, Implementation, Test and Production.
Prototyping Model
The prototyping model is a systems development method in which a prototype (an early approximation of a final system or product) is built, tested, and then reworked as necessary until an acceptable prototype is finally achieved from which the complete system or product can now be developed. This model works best in scenarios where not all of the project requirements are known in detail ahead of time. It is an iterative, trial-and-error process that takes place between the developers and the users.
Initiation Phase
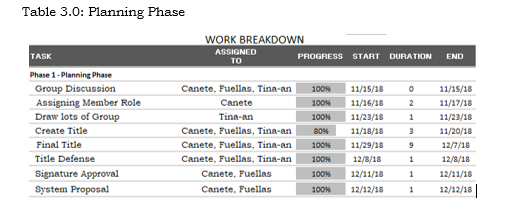
During this initial stage, we select our members to decide what to prioritize. The Project manager assigned the group members to their assigned tasks. After the Project Manager assigned to their designated responsibilities, we decided our capstone title and where we are conducting the title. After that we set an appointment to talk with the Barangay Secretary to approve our title. We also started to make a survey and research about our title to make a documentation and to start our system.
Analysis Phase
The proponents gathered information at the request of the Barangay hall at Barangay Mandalagan. Learning that the residents need to travel and pay Php 20 for their transportation fee. The Proponents figure out the solution about the request of their component.
Design Phase
In scratch to draw us imagine design and we start to do our system. The proponents develop a design which the residents can easily request for their needs. The group decides the system which can know the information, the events, make requests and get reservations. This phase, we imagine our system design and its fiction. Then we use
Implementation Phase
In this phase, the system is already developing and Barangay Mandalagan gives us permission to implement the system and the Barangay Mandalagan check if the system is already working.
Testing Phase
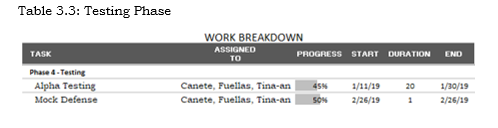
In this phase, the proponents will go through the testing of the input and output of the system. This testing is held where the Barangay has its base. The official of the Barangay are involved in this testing of the system, in which they can profess their opinions and then corrections and adjustments can be implemented. The system is not perfectly function, the proponents gather again information in the barangay and design and for what they want.
Maintenance Phase
This phase is where the system must have an exact date for checking monthly and maintenance to see if it’s working normally, and will continue to provide great service to the Barangay for the future.
Technical Feasibility
Table 2.O: Hardware Requirements(Recommended)
| Hardware | Specification |
| Monitor | Any Brand of LED Monitors Intel Pentium Processor G620 |
| CPU | Minimum 2nd Generation Processor |
| Mouse | USB Mouse |
| Speaker | Multimedia Speaker |
| Memory | 1TB Hard Disk |
Hardware Specification
This system requires the following hardware for the developing of the team and for the usage of end users of the said proposed systems:
| For Project Team |
| LCD or Led Monitors |
| CPU (Dual Processer) |
| Computer Keyboard |
| USB or Optical mouse |
| Multimedia Speakers |
| For End User |
| LCD or Led Monitors |
| CPU (Dual Processer) |
| Computer Keyboard |
| USB or Optical mouse |
| Multimedia Speakers |
Software Specification
This system requires the following software for the development of project team and for the usage of end users of the said proposed systems:
| For Project Team |
| Windows 10 operating system. |
| Adobe dreamweaver CS5 |
| Xampp 1.7.3 |
| Adobe Photoshop CS4 |
| Updated java script compatible browsers such as Mozilla Firefox, Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Safari, Opera Mini and etc. |
| For End User |
| Windows 10 Operating System |
| Xampp 1.7.3 |
| Adobe Photoshop CS4 |
| Updated java script compatible browsers such as Mozilla Firefox, Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Safari, Opera Mini and etc. |
Front End
The proponents used the css for the perfect design and customized the html program.
The proponents used html to have compatible for web browser software and easy way for develop program.
The proponents used bootstrap for the plugins of the system.
Back End
The proponents used php script for the connection for the MySQL database having to insert, select, update, delete and all record from database has to access on php script for to retrieve the data to web page
The proponents used the JavaScript for the real time function to send data and fetching data from the php script and make it to easy and fast load to web page or get data to insert to database without refresh page.
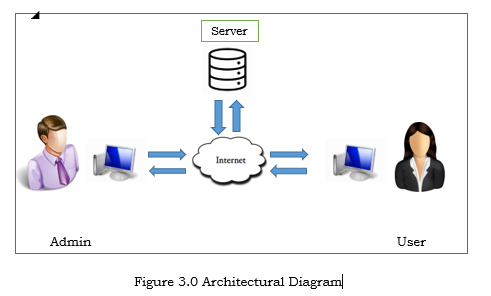
Architectural Diagram
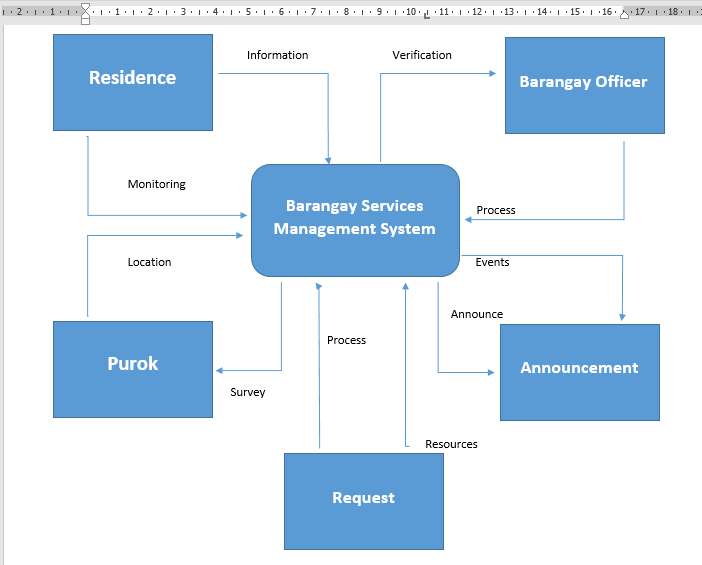
In this figure display the admin that controls the data can add, edit & delete. The User can login, logout, request services update about the events. The Admin will approve the request of the user.
Feasibility Schedule
The Feasibility Schedule contains the record of the users and how they use the system.
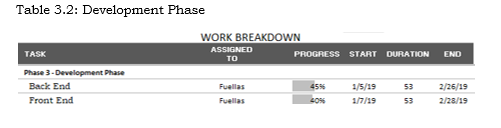
Work Breakdown
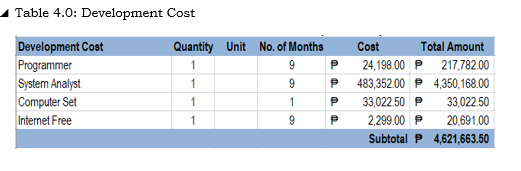
Cost Benefit Analysis
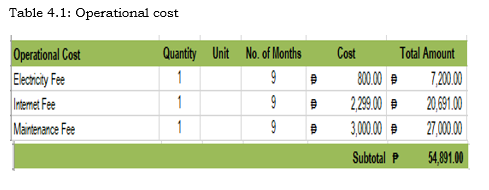
The developmental cost of the system shows that it consists of the person and the other expenses.
This Table shows the Operational cost of the research system. The operational cost includes the maintenance cost and expenditures in using the research system.
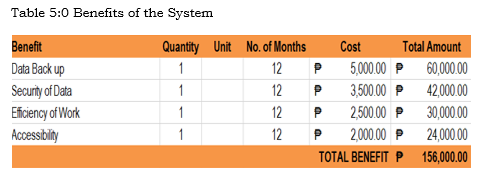
Benefits of the System (Annually) Amount/Value
This table show the total amount of developmental and operational cost of the researched system.
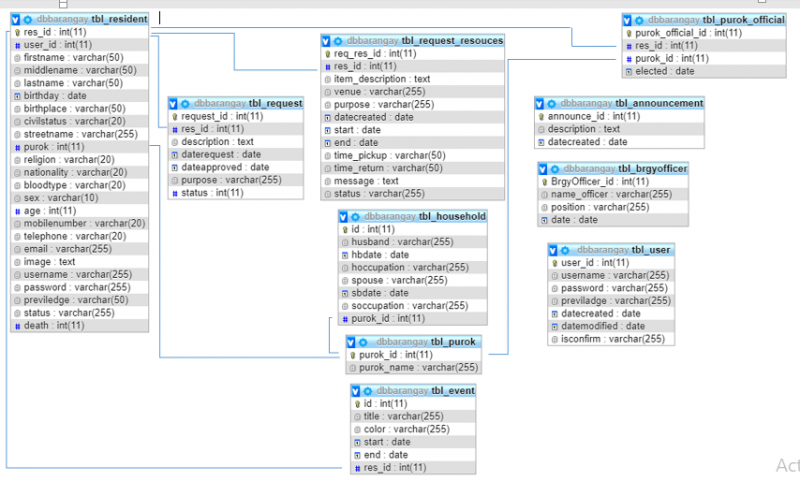
ERD Model
Figure 4.0 ERD
Data Flow Diagram
Figure 5.0 Data Flow Diagram
Data Dictionary
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Length | Constrain |
| announcement_id | int | 11 | Primary key |
| Description | text | None | |
| datecreated | date | none |
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Length | Constrain |
| bCoID | int | 11 | Primary key |
| Officer_Name | varchar | 255 | Not null |
| Scenario | text | none |
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Length | Constrain |
| BrgyOfficer | int | 11 | Primary key |
| Name_officer | varchar | 255 | Not null |
| position | varchar | 255 | Not null |
| Date | date | none |
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Length | Constrain |
| Id | Int | 11 | Primary key |
| Complained_id | int | 11 | Not null |
| Complained | Varchar | 100 | None |
| Complained_age | int | 11 | Not null |
| Complained_address | text | Not null | |
| Complained_contact | Varchar | 20 | None |
| Complainee_id | int | 11 | Not null |
| Complainee
Complainee_age Complainee_address Complainee_contact Incident Date_incident Time_incident Status Recorded Statement User_id |
Varchar
int Text Varchar Text Date Time Varchar Varchar Text int |
100
11 20 100 20 11 |
Foreign key
Not null Not null Not null None None None Not null Not null None Not null |
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Length | Constrain |
| Purok_id | int | 11 | Primary key |
| Purok_name | varchar | 255 | Not null |
| Purok_name | Int | 11 | Foreign Key |
| Eleted | date | 255 |
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Length | Constrain |
| Req_res_id | int | 11 | Primary key |
| Res_id | Int | 11 | Foreign Key |
| Item_description | Text | None | |
| Venue | varchar | 255 | Not null |
| Purpose | varchar | 255 | Not null |
| Datecreated | date | 50 | Not null |
| Start | date | 20 | Not null |
| End | date | 255 | Foreign key |
| Time_pickup | varchar | 50 | Foreign key |
| Time_return
Status |
varchar
varchar |
50
255 |
Not null
Not null |
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Length | Constrain |
| Purok_official | int | 11 | Primary key |
| Res_id | Int | 11 | Foreign key |
| Purok_id | Int | 11 | Foreign key |
| Eleted | date | 255 | Not null |
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Length | Constrain |
| Id | Int | 11 | Primary key |
| Title | varchar | 255 | Not null |
| Color | Varchar | 255 | Not null |
| Start | Date | Not null | |
| End
Res_id |
Date
int |
11 | Not null
Foreign key |
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Length | Constrain |
| User_id | Int | 11 | Primary key |
| Username | varchar | 255 | Not null |
| Password | varchar | 255 | Not null |
| Previledge | varchar | 255 | Not null |
| datecreated
datemodified |
date
date |
Not null
Not null |
|
| isconfirm | varchar | 255 | Not null |
Table 6.9: Barangay clearance officer
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Length | Constrain |
| bCoId | Int | 11 | Primary key |
| Officer_Name
Scenario |
Varchar
text |
255 | Not null
None |
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Length | Constrain |
| Res_id | Int | 11 | Primary key |
| firstname | Varchar | 50 | Not null |
| Middlename | Varchar | None | |
| Lastname | Varchar | 255 | Not null |
| Birthday | Date | 255 | Not null |
| Birthplace | Varchar | 50 | Not null |
| Civilstatus | Date | Foreign key | |
| Streetname | Varchar | 255 | Not null |
| Purok | Int | 11 | Foreign key |
| Religion | Varchar | 20 | Not null |
| Nationality | Varchar | 20 | Not null |
| Bloodtype | Varchar | 20 | Not null |
| Sex | Varchar | 10 | Not null |
| Age | Int | 11 | Foreign Key |
| Mobilenumber | Varchar | 20 | Not null |
| Telephone | Varchar | 20 | Not null |
| Varchar | 20 | Not null | |
| Image | Text | Not null | |
| Username | Varchar | 255 | Not null |
| Password | Varchar | 255 | Not null |
| Privilege | Varchar | 50 | Not null |
| Status | Varchar | 255 | Not null |
Table 7.1: Barangay clearance officer
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Length | Constrain |
| bCoId | Int | 11 | Primary key |
| Officer_Name
Scenario |
Varchar
text |
255 | Not null
None |
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Length | Constrain |
| Mgs_Id | Int | 11 | Primary key |
| Clearance_id | int | 11 | Not null |
| message | text | Not null | |
| datemodified | Datetime | Not null |
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Length | Constrain |
| Id | Int | 11 | Primary key |
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Length | Constrain |
| Id | Int | 11 | Primary key |
| Resident_id | int | 11 | Not null |
| Fullname | Varchar | 50 | Not null |
| Status | varchar | 50 | Not null |
| Field Name | Data Type | Field Length | Constrain |
| Tanod_duty_Id | Int | 11 | Primary key |
| Tanod_id | int | 11 | Not null |
| location | text | Not null | |
| Date_start | Date | Not null | |
| Date_end
Date_modified |
Date
Date |
Not null
Foreign key |
Presentation, Analysis, And Presentation Of Data
This chapter exhibits the results of the User’s Survey conducted for the system to the Barangay Mandalagan Officials and residence.
Presentation
The proponents demonstrate the system’s functionality to the randomly selected respondents. The proponents observed the respondents on how they response to the system. The respondents were evaluated using the User Acceptance Survey in order for the respondents to distinguish the level of acceptability of the proposed system.
Data Analysis
This section presents the analysis of the data collected and gathered from the respondents of the Barangay Mandalagan Officials and residence.
Characteristics of the Respondents
Table 8.0. Frequency of Respondents
Respondents Frequency
Barangay Chairman 1
Barangay Secretary 1
Barangay Kagawad 7
Barangay Tanod 5
Barangay Staff 5
Barangay Residence 11
Total 30
The population composed of the Barangay Chairman, Secretary, Kagawad, Tanod, Staff, and Residence. The proponents got thirty respondents from Barangay Mandalagan. The proponents use a convenience sampling, where it surveys the 11 residence only. Table 8.0 shows the number of respondents who have answered the User-Acceptability Survey. The researchers got a total of 30 respondents.
Interpretation of Data
Range of Mean Verbal Interpretation
4.21-5.00 Very Satisfied
3.41-4.20 Satisfied
2.61-3.40 Dissatisfied
1.81-2.60 Very Dissatisfied
1.00-1.80 Poor
The adopted survey instrument determined the acceptability of the system in terms of (5) categories namely: Effectiveness, Efficiency, Quality, Timeliness and Productivity. The first category was composed of (4) items, the second category was composed of three (3) items, and the third, fourth and last category were composed of four (4) items. Table 9.2 and 9.5 shows that the user’s survey result for the systems quality came back with the total mean of 4.5 which interpret that the users were satisfied with the system’s quality after testing it.
Effectiveness
Table 9.1: Survey Result – Effectiveness
System Quality Performance Total Mean Verbal Interpretation
Table 9.1 shows that the user’s survey result for the effectiveness of the system came back with a total mean of 4.0 which is interpreted as “Satisfied” which means that the end-users were satisfied with the system’s effectiveness after testing it.
The respondents stated that the proposed system (BSMS) meet the desired result and it produced the desired output. They desired stated that the system is effective, it means it has an intended or expected outcome.
Efficiency
Table 9.2: Survey Result – Efficiency
System Quality Performance Total Mean Verbal Interpretation
Table 9.2 shows that the users survey result for the system’s efficiency came back with a total mean of 4.5 which interpret that the users were Very Satisfied with the efficiency of the system after testing it.
The respondents stated that the system (BSMS) has the ability to maximize their work, time consuming and easier for the community to access. In a more general sense, the system (BSMS), has the ability to do things well, successfully, and all that can make system make better.
Quality
Table 9.3: Survey Result – Quality
System Quality Performance Total Mean Verbal Interpretation
Table 9.3 shows that the user’s survey result for the system’s quality came back with the total mean of 4.0 which interpret that the users were satisfied with the systems quality after testing it.
The respondents stated that the system (BSMS), meet the standards of the users in terms of its degree of excellence.
Timeliness
Table 9.4: Survey Result – Timeliness
System Quality Performance Total Mean Verbal Interpretation
Table 9.4 shows that the user’s survey result for the system’s timeliness came back with a total mean of 4.0 which interpret that the users were satisfied with the systems timeliness after testing it.
The respondents stated that the system (BSMS), has the quality in generating and recording reports.
Productivity
Table 9.5 Survey Result – Productivity
System Quality Performance Total Mean Verbal Interpretation
Productivity 4.5 Very satisfied
Table 9.5 shows that the user’s survey result for the system’s productivity came back with the total mean 4.5 which interpret that the users were very satisfied with the system’s productivity after testing it.
The respondents stated that the system (BSMS) has the ability to produce a desired result where they measured the ratio of output to inputs used in a production process, i.e. output per unit of input.
Over All
Table 9.6 Survey Result – Over All
System Quality Performance Total Mean Verbal Interpretation
Overall 4.2 Satisfied
Table 9.6 calculated the overall categories of the system’s acceptability and it resulted to as 4.2 which means as “Satisfied” that the users were very pleased with how system functioned in all service.
Summary Of Findings, Conclusion And Recommendation
This chapter presents the summary of the findings, and the conclusions and the recommendations for the system study.
Summary of Findings
This study was conducted for the purpose of Barangay Services Management System for Barangay Mandalagan, to objectively result to a faster and effective services to the Barangay Mandalagan. The descriptive method of research was utilizing and the survey technique was used for gathering data. A questionnaire served as an instrument for the collection of data.
The proponents conducted a survey to the Barangay Mandalagan. The participants were the Barangay Captain, Kagawad, Staff, Tanod, Barangay Secretary and Residence. The survey was conducted after the system had all the requirements, functionalities and features embedded.
The findings suggested that on the level of the user’s experience in terms of effectiveness of the system a mean score of 4.0 was obtained and interpreted as “Satisfied”. As to the experience of the user in the efficiency category, it obtained a mean of 4.5, it interpreted “Very Satisfied”. On timeliness category, the users gave a mean of 4.0 interpreted as “Satisfied”. On productivity category, the users gave 4.5 interpreted as “Very Satisfied”. In overall, the systems rating is collected a mean of 4.2 is interpreted as “Satisfied” rating.
Conclusion
The proponents conclude that the system is fully operational and dynamic, as of the sum, data gathered. This condition is on the premise that it has addressed the necessary automation requirement of the firm after the thorough system study.
Recommendations
- The admin should train of using the computer and to the software
- Maintenance should be monthly.
Credits
Cañete, Jessa Mae, P.
Fuellas, Jose Francis, D.
Tina-an, Jessa Mae, M.





Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.