Queuing System Capstone Project Document
Introduction
These days, the world depends on technology and each person from young to old are seem to be deeply involved. Technology is one of the important components in today’s society and it makes the daily activities easier. It is true that all sector of society was impacted to increase efficiency and effectiveness. All business companies have their own strategy to serve a client but currently, technology has a process called queue that provides a customer service in convenient way. Queuing system is to control clients at the counters where their priority number appeared on screen.
ABC has an existing manual queuing system which was used in enrollment process. According, to our observation of getting the priority number is a waste of time because you need to fall line in the last person who also getting a queueing number. The person-in-charge needs to ask what transaction you are about to make and need to encode the student’s number to proceed the other window to accommodate by person-in-charge per window. The number in LED monitor are displayed randomly that give student anxiety.
ABC Online Queuing System (ABC OQS) is a queuing processes which make it easy for students to set appointments and wait from anywhere. That means students can make an appointment online, receive communications and alerts via SMS notification, and even rate them experience on a handheld device before they leave the environment. A well-managed and fair waiting environment keeps students aware of how long it will take before they are served. Clear, honest communication eases anxiety, making students more comfortable with their wait, and supports a more efficient and productive environment. This study aims to develop a system which set to organize, engage, & measure waiting and improve student’s involvement satisfaction.
Background of the study
ABC Campus has many students enrolled every year. Long waiting remains a major issue during enrollment. This is because students who cannot be served immediately have to fall in line for service and the time could range from few minutes to long hours. The proponents conducted a study about ABC Registrar’s Office on using manual process. Time-saving and convenience are commonly mentioned by students that could results dissatisfaction. This is why the researcher proposed a ABC Online Queueing System with SMS notification.
Objectives of the Study
The study aims to develop an Automated Queuing System for ABC Campus.
Specifically, the following are the specific objectives:
1. Develop a queuing system that will maximize the efficiency of service to the students by creating a centralized and dynamic queue based on staffing.
2. Develop a queuing system that will reduce the time spent in lines and queues.
3. Generate statistical reports that will provide complete information in terms of:
a. The time and the number of students served in a specific period of time
b. Employees efficiency result in terms of the number of students served
4. Develop a dynamic queuing system that can address different situations and needs (e.g. assigning student needing service case numbers and priority statuses)
Conceptual Framework
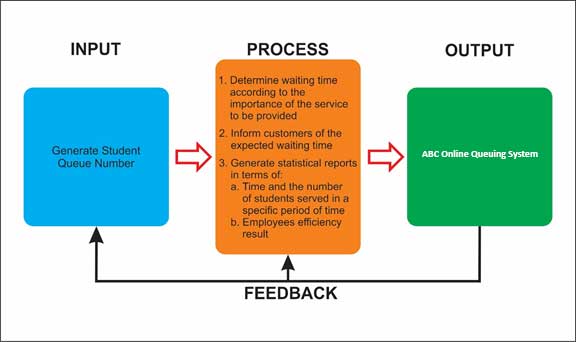
This study intends to process the enrollment less demanding and change over through automated system. ABC is a local system that can be gotten to by two sorts of end users. The staff that is appointed to generate student queue number and administrator for the support of the system. This system can determine waiting time according to the importance of the service to be provided, inform customers of the expected waiting time and generate statistical reports in such as time and the number of students served in a specific period of time, employees efficiency result.
Figure 1: Conceptual Framework of ABC Online Queuing System
Scope and Delimitation of the Study
This section enumerates the scope covered by the study and its delimitation.
Scope
The study covers ABC – (ABC) that focuses on the issue of waiting time and services during enrollment. This system will provide a sequential priority number to the students upon arrival, recording arrival time and service time were done automatically. Through this system, it will help to lessen the long waiting time through:
• Identify the number of students served in a specific time.
• Providing a priority lane and number to the PWD’s, pregnant women, and Senior Citizen.
• Notifies students through SMS.
• Monitors the sequential number through mobile devices.
• Generate statistical reports.
Through this, it will help to maximize the efficiency of service to the students.
Queuing System Capstone Project Document Delimitation
This study is limited to the registrar’s office of ABC and the two end user:
• Administrator and
• Approved Staff to use the system.
• The system does not cover the computation of student’s rating
• Class scheduling
• Viewing of subjects and teachers and paying of fees
• Not accepting any online payments
• It can only operate for school enrollment purposes
• It can’t show the schedule of the subject in per year level.
Significance of the Study
This study is intended to various set of people who could benefit in the system. The result of this study will be beneficial to the following:
Registrar Office. This system will provide efficient and effective transactions through an organized system; authority of monitoring and control the number of students. This system will be beneficial to management in lessening the time effort.
Personnel In-charge. This study aims to minimize their work load. This system will also save student waiting in line.
Student. This system will be beneficial to the students in terms of securing the priority number in server.
Proponents. This system will enable them to apply what they have studied and researched.
Future Researcher. The study will significant to the future researchers. The system can be used by researchers as a reference for the future projects.
Queuing System Capstone Project Document Definition of Terms
Conceptual. A statement or description of the fundamental character or scope of something. (“Merriam – Webster Dictionary”, n.d)
Database. Conceptually, is a collection of information that is organized so that it can easily be accessed, managed, and updated. (“Techtarget.com”, n.d)
Dynamic. (Of a process or system) characterized by constant change, activity, or progress. (xforddictionaries.com)
Queue. A sequence of messages or jobs held in temporary storage awaiting transmission or processing. (“Merriam – Webster Dictionary”, n.d)
Queuing System. Control the number of the students to done a process of transaction
Sequential. Forming or following in a logical order or sequence. (oxforddictionaries.com)
System. As used in the study, this term refers to the method of flow in all the transactions of the ABC Registrar’s in terms of monitoring the number of students enrolled.
Review Of Related Literature
This chapter discusses the existing study into the context of proceeding related research. These research study cited articles and systems, which are pragmatic that are based on research and design of the developer to meet the user’s need.
Local Related Study
QueueRite System
QueueRite is a complete enterprise software system for customer queue management system. This software allows businesses to systematize the procedure for customers as they line up and wait for their turn to be served. By using the Queuerite software, customer services at the reception area will become more efficient and the confusion brought by customers’ long lines will be minimized. SMS Capability that allow the customers more convenience while waiting for their turn, our system can send out SMS notifications as the customer’s queue number is getting near. Software Customization to recognize that each business is unique, so the queuing software can be configured to your specific needs. In-house programmers that can customize the features and functionalities of the existing QueueRite System to specifically suit the requirements of your business. Security-enabled the Ivant Queue Management System requires a username / password log-in as an initial security feature. The starting numbers for queuing are also randomized to further safeguard the queuing process. (“Customer Queue Management System, Leading Enterprise Software with SMS Notifications and Online Appointments.” Accessed March 17, 2018.)
Development of Payment Queuing System with Android Application
Transactions involving basic utilities have long been universally accepted to constitute long waiting-lines. This could be observed in health services, government offices and school enrollment procedures. However, more often than not, taking DLSU-D enrollment seasons to be observed and serve as an example, the mixing of minor and major transactions not only lengthens the waiting-lines longer than is necessary, but also inconvenience students only requiring simple and non-time-consuming transactions as well as leaving them stranded. The group decided on pursuing “Development of Payment Queuing System with Android Application” to help solve and alleviate these issues through transaction categorization and separation, and service time estimation functionalities.
The system had 4 different types of application developed, namely: a server program; client terminal application; cashier program; and an android application.
The system as a working whole was composed of a client program that accepts user input regarding transaction information, a MySQL server serves as a backend database, and a P.O.S (point of sale) program allows the user to view and process transactions in queue. In addition, a separate notification program outputs to a monitor the current transactions being serviced and its corresponding P.O.S terminal, it also displays as well the current queue length of both minor and major transactions. The interfacing of all involved components is managed by a wireless router hosting a local area network. All components are connected through cat5 cables with the exception of the android client program which interacts wirelessly. (“Development of Payment Queuing System with Android Application.” Accessed March 17, 2018.)
Bank of the Philippine Islands Express Assist (BEA) Online
BEA Online is an off-shoot of the BPI Express Assist (BEA) terminals installed in the branches. BEA eliminates the need to fill-up paper forms since it now allows branch customers to input their branch transaction details into a touch-screen terminal instead. Upon submission, the transaction details are automatically transmitted to the tellers and customers are issued queue numbers. Rather than waiting in line, customers can just sit down and relax while waiting for their queue numbers to be called.
This facility has effectively reduced the customers waiting time at the branch. Likewise, with BEA Online, customers can now choose time-slots for their branch transactions in advance. Customers simply need to log-in to www.bpiexpresssonline.com, click on Other Services, and then click on BPI Express Assist Online. After which they may choose their preferred BPI branch, date, and time for they will fulfill the transaction, then input their transaction details. Electronic queue numbers will be issued for the Deposit, Withdrawal, Encashment, or Bills Payment Transactions they encoded online. (“Pattawi, Jarel. “II.RELATED LITERATURE REVIEW.” Accessed March 17, 2018.)
Foreign Related Concept/Studies
Wireless remote queuing system and method
The disclosure describes methods and systems of allowing people to virtually queue in a line via text messaging or mobile phone calls. The person wishing to get in the line sends a text message or cellphone call to queuing system. Alternatively, the person can register via a computer network connection. The queuing system the sends a text message back to that person when it is nearly time for them to receive the benefit of being at the front of the time. (Backer, Alejandro, and Timothy Ross McCune. Wireless remote queuing system and method. United States US20080133283A1, filed November 16, 2007, and issued June 5, 2008. )
Automatic Queuing Model for Banking Applications
Queuing is the process of moving customers in a specific sequence to a specific sequence to a specific service according to the customer need. The term scheduling stands for the process of computing a schedule. This may be done by a queuing based scheduler. This paper focuses on the bank lines system, the different queuing algorithms that are used in banks to serves the customers, and the average waiting time. The aim of this paper is to build automatic queuing system for
Organizing the banks queuing system that can analyses the queue status and take decision which customer to serve. The new queuing architecture model can switch between different scheduling algorithms according to the testing results and the factor of the average waiting time. The main innovation of this work concerns the modeling of the average waiting time is taken into processing, in addition with the process of switching to the scheduling algorithm that gives the best average waiting time. (S.A, Ahmed, and Dr. Huda. “Automatic Queuing Model for Banking Applications.” International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications 2, no. 7 (2011).)
Automated Queue Management System
Automated queue management system is a system that helps service provider to manage customers in efficient way. The system can ease the customer flow management which is useful for manager of the service provider. The purpose of this project is to develop an Automated Queue Management System for organizing queuing system that can analyze the queue status and take decision which customer to be served first.
This project focuses more on the banks queuing system, different queuing algorithm approaches which are used in banks to serve customer and the average waiting time. This queuing architecture model can switch between different scheduling algorithms according to the testing result i.e. the average waiting time by using two different queue control systems, which have developed. There are several process undergo, which control by Intel Galileo Microcontroller that is software-compatible with the Arduino software development environment. Finally, the systems have been tested under different conditions to evaluate its performance. (Uddin, Md.Nasir, NA Nithe, and SZ Ahmed. “Automated Queue Management System.” Global Journal of Management and Business Research 16 (December 31, 2015): 51–58.)
Related Systems
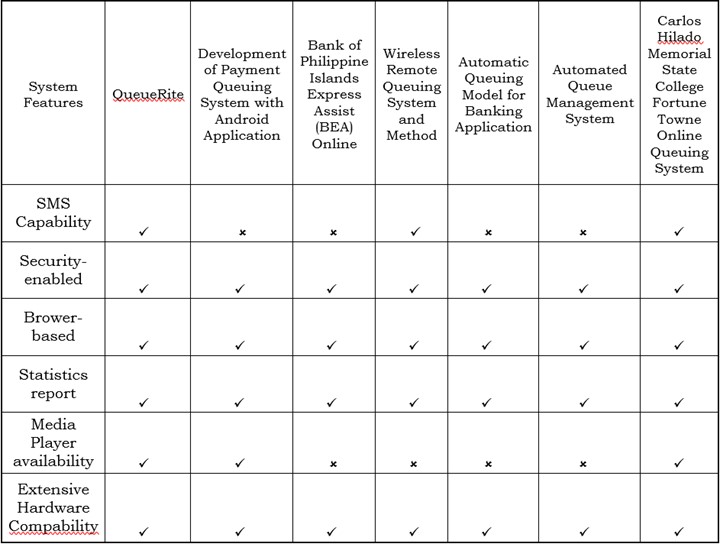
Table 1: Related Systems
Table 1 shows features of the proposed system in the first column, whereas the following columns are the features of the related systems.
Synthesis
The system that was presented were obtained from both foreign and local system that we made basis for creating the queuing system. It additionally portrays a features that accessible on the system and the next system who does not accessible to have.
All the related system discussed the different characteristics of the system that helps to manage the customers in efficient way. The systems innovation work concerns the factors of the average waiting time. Also we observed absence of security in keeping the records and statistical reports.
The system discussed are correlated to the proponent’s system, the ABC Online Queuing System. The researchers analyzed precisely and assessed the related system based on its modules and its functions.
The related system has made the proponents realized some capacities and factors that would help the proposed system to be further developed, efficient and effective for the users. Furthermore, the proponents gather some features in the related study and merged it to the system to be greater beneficial for each students and staff in Registrar’s office.
Methodology
This chapter discusses the research strategy and procedures on how the system flows and its process. Through interview and observation about the present and existing condition the fundamentals in the development of the proposed system for ABC- ft Online Queuing System was determined. This chapter include overview how to treat research data by researchers.
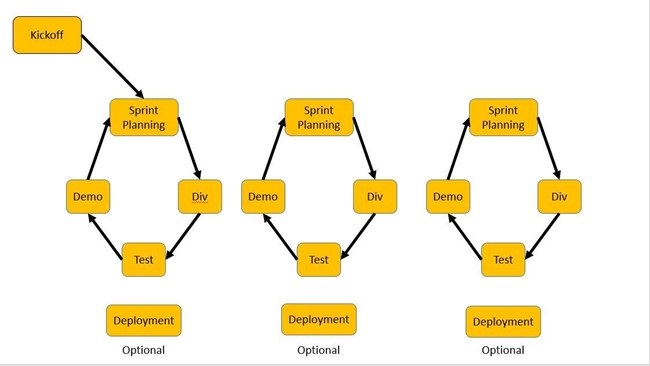
The proponents follow the standard System Development Life Cycle (SDLC), to define and present solutions for the problems identified in this study, using the agile model.
In this model, the stages show the connection to the proposed system through sequential flow that each phase needs to be completed first before going to the next phase.
The system development process model is broken down into different phases. Basic phases of system development processes are as follows: sprint planning, development, testing, demonstration and deployment.
Sprint Planning Phase
This is the first phase where the most critical part in completing the proposed system. The proponents observed and gathered data in order to identify the needs of ABC registrar’s office. The proponents also coordinate to identify the problems, the scope and objectives of the study by conducting interviews from the Registrar’s Office, The Registrar, and Staff. The problems identified by the proponents studied carefully to understand and evaluate the difference between the present existing system and the proposed system. The leader assigned their roles and responsibilities to do their tasks. The gathered information where combine to make basis for creating the Chapter 1 for the objectives of the system and Chapter 2 for the related basis of the said system.
Development Phase
In this phase, the proponents gathered information allows to design and develop a system. The team manager assigned to each members to create the Chapter 3 that includes Methodology, Technical Feasibility, Context Diagram, Data Flow Diagram, Entity Relationship Diagram and Cost Benefit Analysis. Development Phase the programmer use a programming language to run the system through HTML5, PHP, CSS Ajax. (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) and Xampp: 3.2.1 version (Apache, MySQL).
Figure 2: Agile Model
Technical Feasibility
Hardware Requirements (Recommended)
Server
• Hard disk: More than GB
• Memory: 4GB or Higher
• Processor: Pentium Quadcore or higher
• Monitor: Recommended 1366 x 768
• Mouse
• Keyboard
• Network: LAN
Client
• Hard disk: More than 500GB
• Memory: 1GB or Higher
• Processor: Dual core or higher
• Monitor: Recommended 1366 x 768
• Mouse
• Keyboard
• Printer: Thermal
• Network: LAN
Software Requirements (Recommended)
Server
• Operating System: Windows 7 or Latest
• Browser: Firefox, Google Chrome
• Xampp: 3.2.1 version (Apache, MySQL)
Client
• Operating System: Windows 7 or Latest
• Browser: Firefox, Google Chrome
Program Environment
Front End
HTML5. Hypertext Markup Language, is the latest evolution of the standard that defines HTML. The term represents two different concepts. It is a new version of the language HTML, with new elements, attributes, and behaviors, and a larger set of technologies that allows the building of more diverse and powerful Web sites and applications.
CSS. Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a style sheet language used for describing the presentation of a document written in a markup language. A cascading style sheet (CSS) is a Web page derived from multiple sources with a defined order of precedence where the definitions of any style element conflict.
Ajax. (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) Is a set of web development techniques using many web technologies on the client-side to create asynchronous Web applications. With Ajax, web applications can send data to and retrieve from a server asynchronously (in the background) without interfering with the display and behavior of the existing page. By decoupling the data interchange layer from the presentation layer, Ajax allows for web pages, and by extension web applications, to change content dynamically without the need to reload the entire page. Read data from a web server after the page has loaded. Update a web page without reloading the page and send data to a web server – in the background
Back End
HTML5. Hypertext Markup Language, is the latest evolution of the standard that defines HTML. The term represents two different concepts. It is a new version of the language HTML, with new elements, attributes, and behaviors, and a larger set of technologies that allows the building of more diverse and powerful Web sites and applications.
CSS. Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a style sheet language used for describing the presentation of a document written in a mark-up language. A cascading style sheet (CSS) is a Web page derived from multiple sources with a defined order of precedence where the definitions of any style element conflict.
Ajax. (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) Is a set of web development techniques using many web technologies on the client-side to create asynchronous Web applications. With Ajax, web applications can send data to and retrieve from a server asynchronously (in the background) without interfering with the display and behavior of the existing page. By decoupling the data interchange layer from the presentation layer, Ajax allows for web pages, and by extension web applications, to change content dynamically without the need to reload the entire page. Read data from a web server after the page has loaded. Update a web page without reloading the page and send data to a web server – in the background
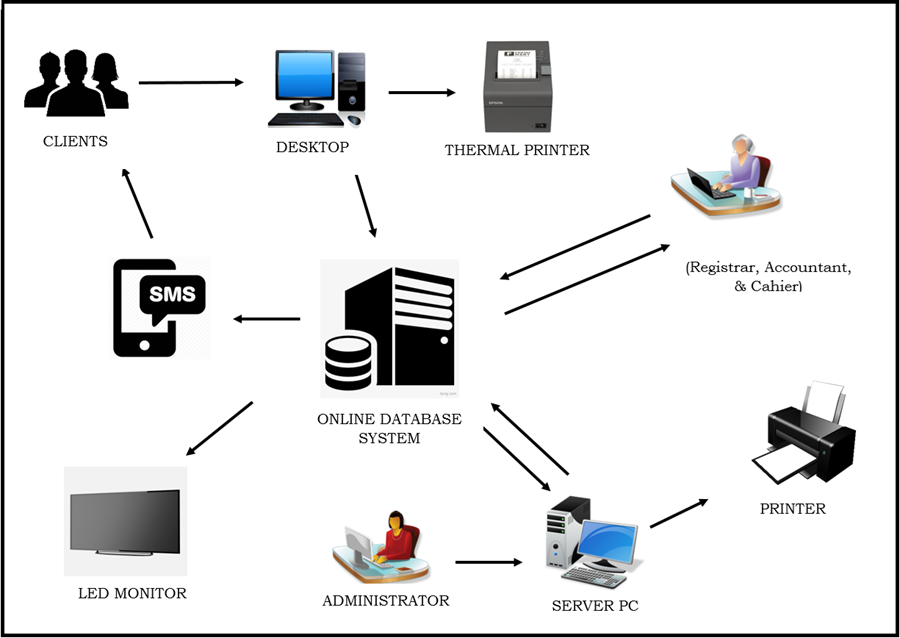
Architectural Diagram
Figure 3: Architectural Diagram of ABC Online Queuing System
Feasibility Schedule
The feasibility schedule contains the record of the amount of time the proponents spent on the system.
Gantt Chart
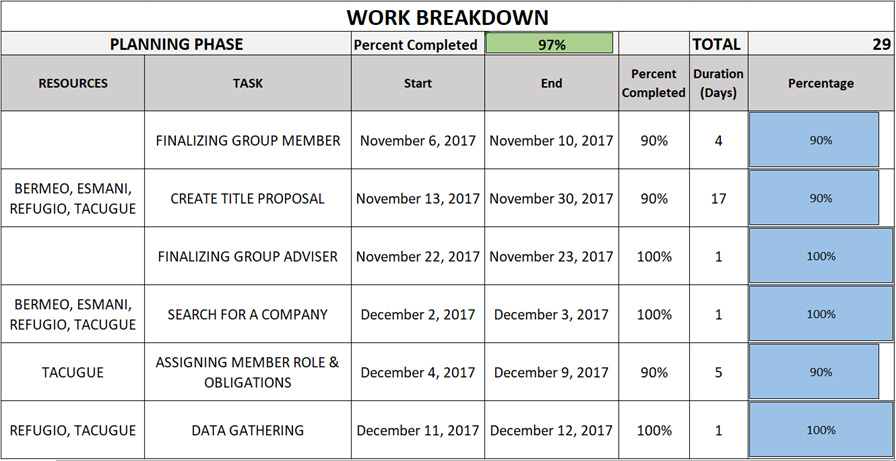
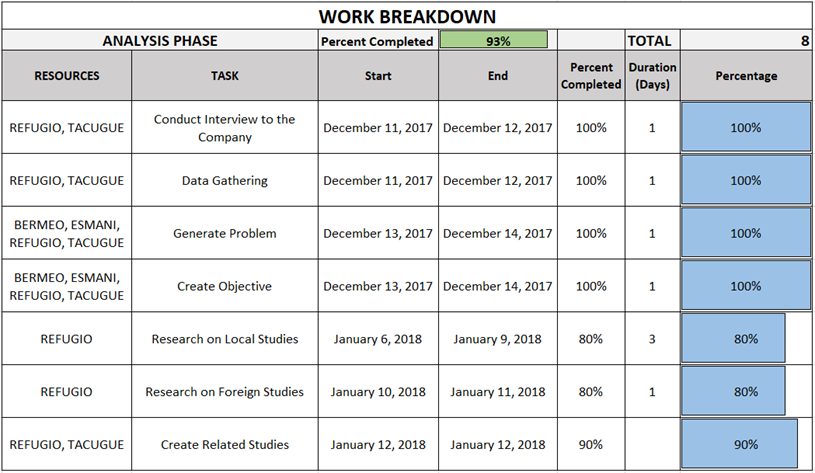
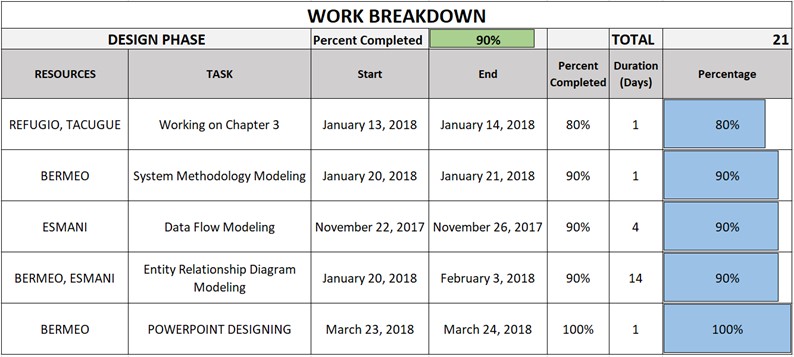
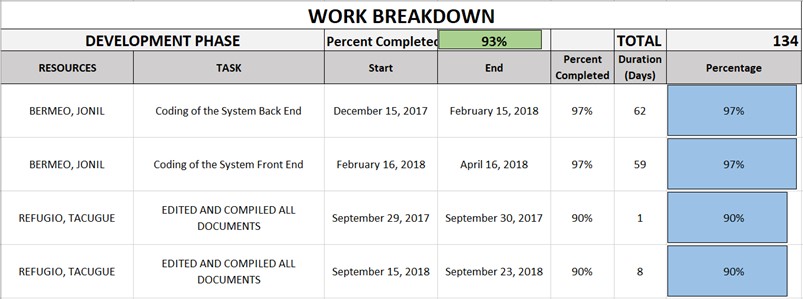
The following tables show the Gantt chart of the tasks that have been done by the proponents with the time allotted for the establishment of the entire system.
Table 2.0: Planning Phase
Table 2.1: Analysis Phase
Table 2.2: Design Phase
Table 2.3: Development Phase
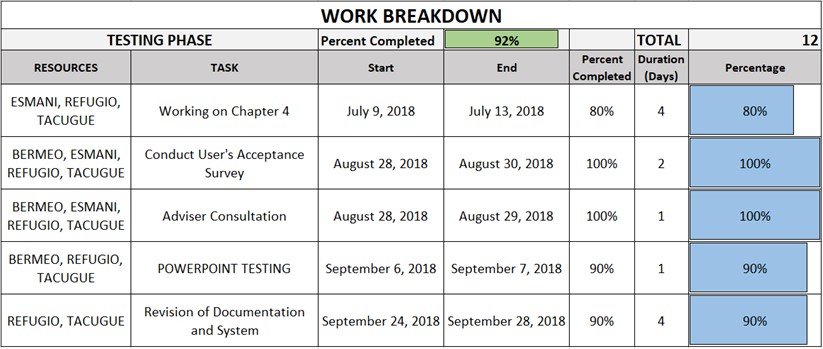
Table 2.4: Testing Phase
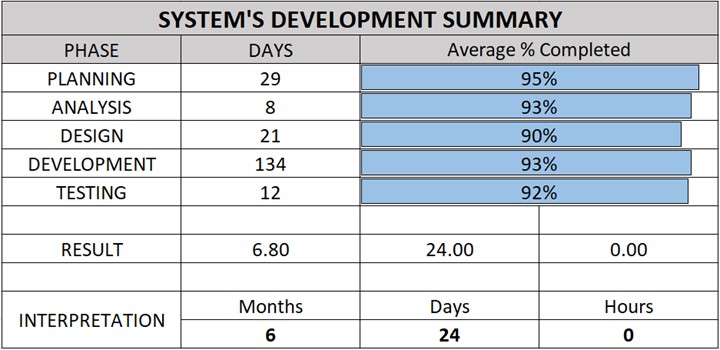
Table 2.5: Software Development Summary Phase
Cost Benefit Analysis
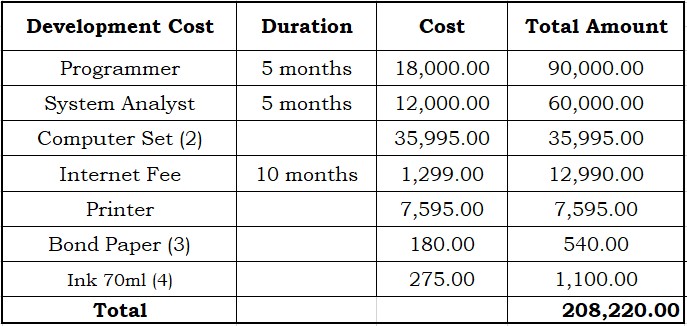
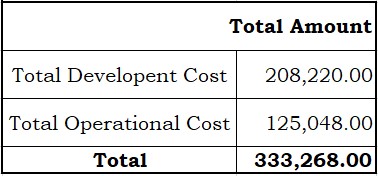
Table 3.0: Developmental Cost
Cost benefits analysis or the CBA, is the estimated cost and sum of the amount cost and benefits of the system, to determine whether the company can gain benefit from the system.
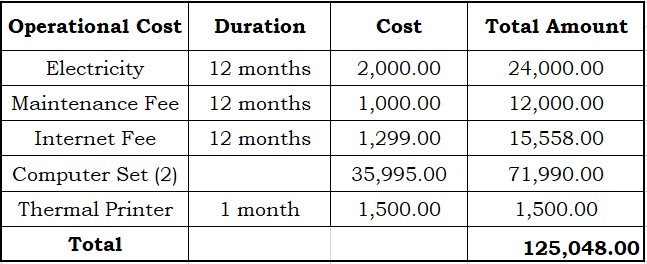
Table 3.1: Operational Cost
This table shows the Operational cost of the researched system. The operational cost includes the maintenance cost and expenditures in using the researched system.
Table 3.2: Total Developmental Cost
This table shows the total amount of developmental and operational cost of the researched system.
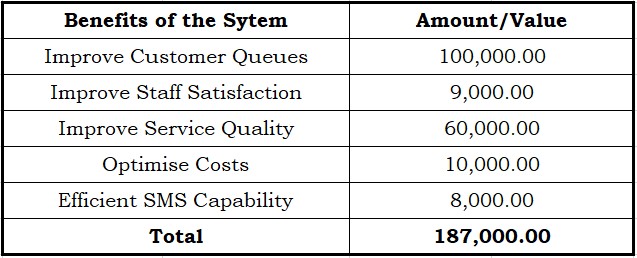
Table 3.3: Benefits of the System
This table shows the computed benefits of the researched system to the company. The proponents have researched on what are the
presumed amounts or value of each item that will benefit the company
over its traditional method per year.
Cost Benefit Analysis
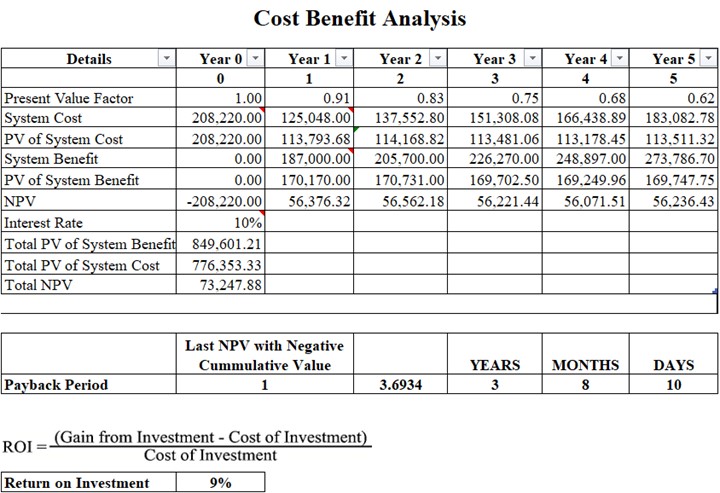
Table 3.4: Cost Benefit Analysis
Table 2.4, shows a chart of the Cost and Benefits analysis. The Return of Investment comes out of 9%. The Payback Period was computed by taking the sum of the Present Value of system Benefit (Php170,170.00) subtracting it to the Present Value of System Cost (Php113,793.68) to get its Net Present Value and get the sum of Net Present Value (Php56,376.32) subtracting it to the negative value of System cost (Php-208,220.00), and dividing the difference Net Present Value (Php56,376.32). Resulting to 3.6934 which is round to 3, making it a 3-year payback period. Payback period = Initial Investment/Cash Inflow. The ROI was computed by taking the sum of the Total Present Value of system benefits (Php849,601.21), subtracting it to the Total Present Value of System Cost (Php776,353.33), and dividing the difference Total Present Value of System Cost (Php776,353.33). The quotient is Php849,601.21 which is equivalent to 9% of ROI or Return of Investment. The formula that the proponents used can be seen on Table 3.4.
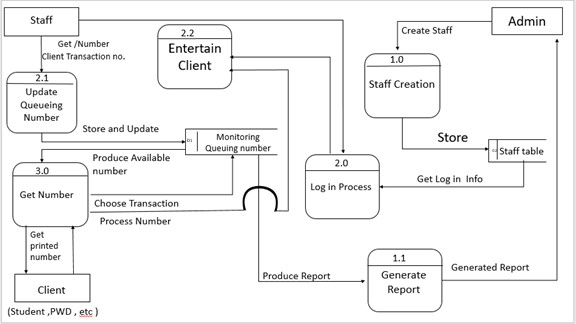
Data Flow Diagram (Gane-Sarson)
Figure 5: Data Flow Diagram of ABC Online Queuing System
Database Dictionary
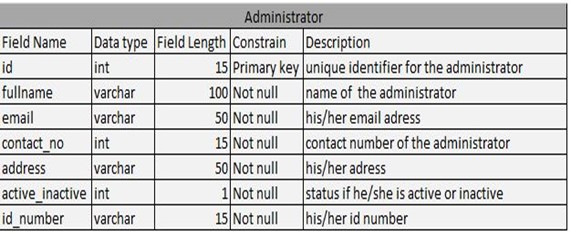
Table 4.0: Administrator Table
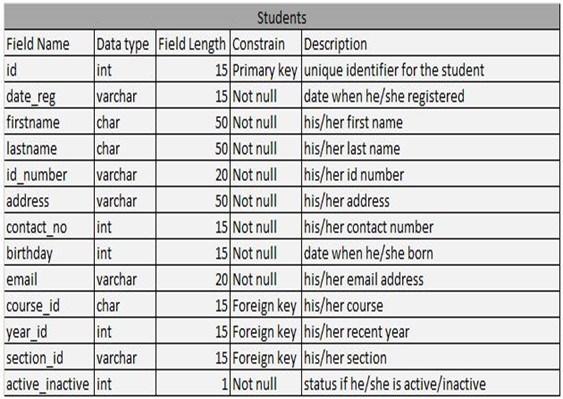
Table 4.1: Students Table
Table 4.2: SMS Record Table
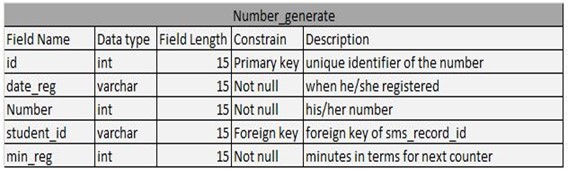
Table 4.3: Number Generate Table
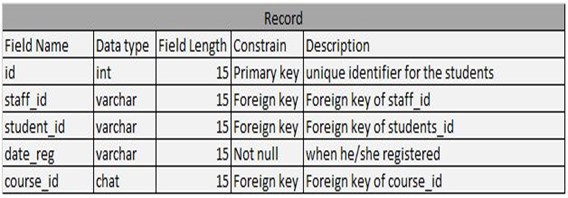
Table 4.4: Record Table
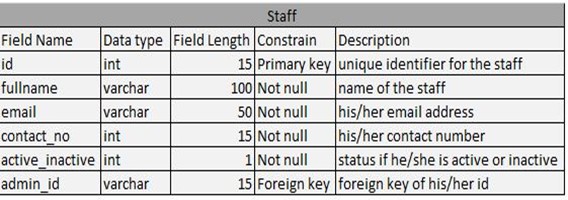
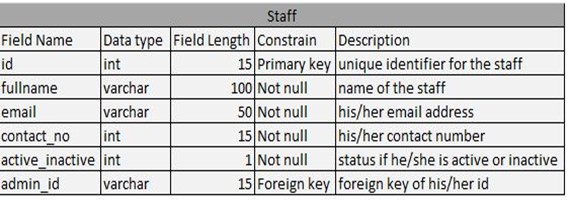
Table 4.5: Staff Table
Table 4.6: Queuing Process Table
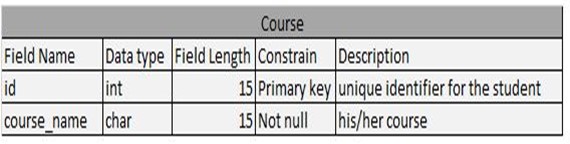
Table 4.7: Course Table
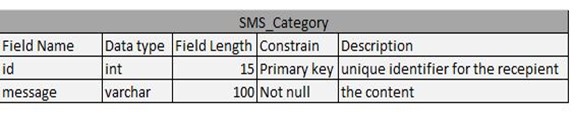
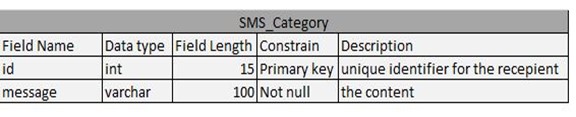
Table 4.8: SMS Category Table
Table 4.9: Year Table
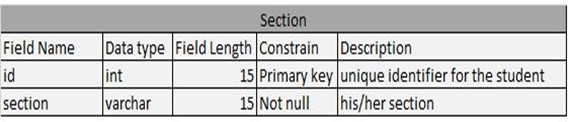
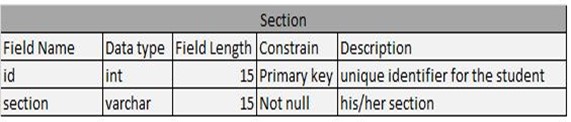
Table 4.10: Section Table
Database Model
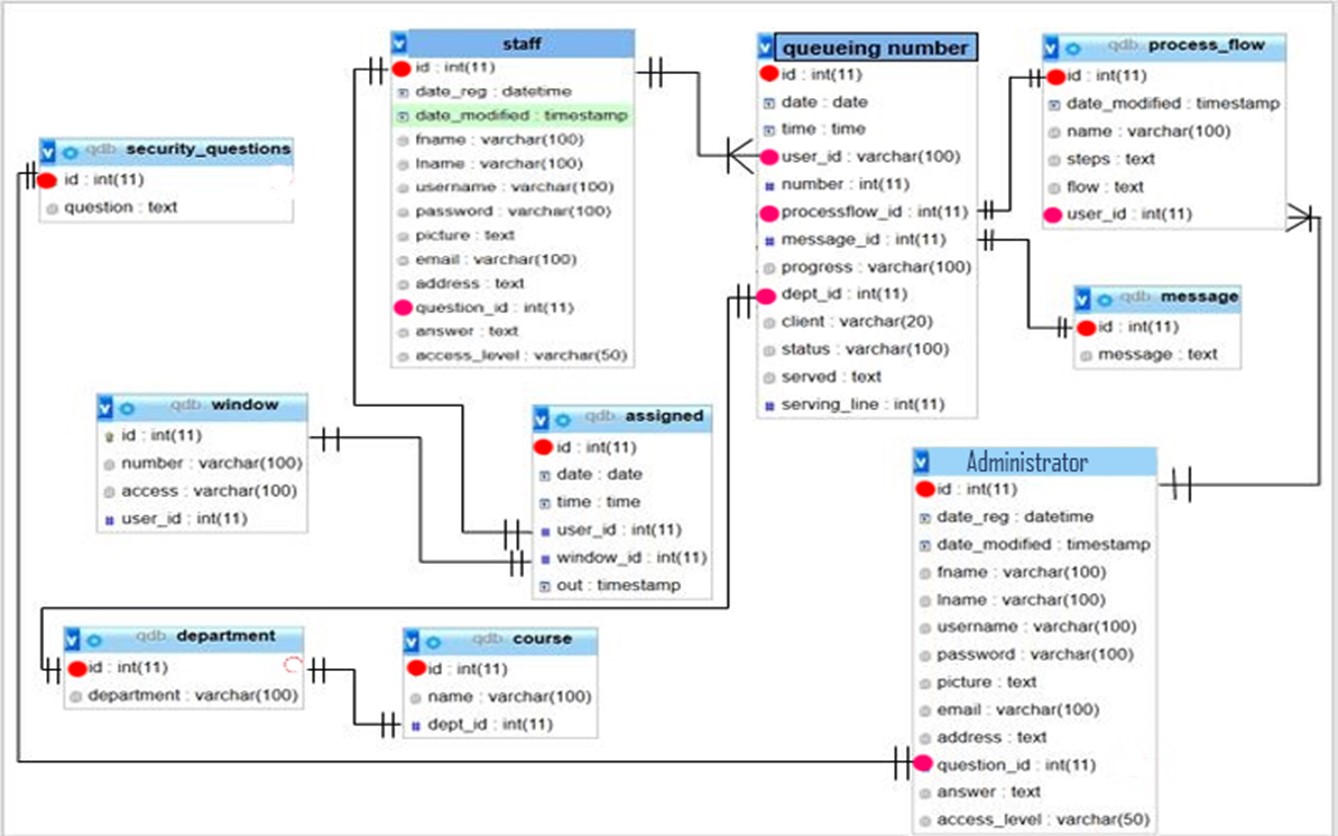
Entity Relationship Diagram
Entity Relationship Diagram explains every relationship between table’s entity and attributes. Each table has a definition that connects every table, both its primary key and foreign key. Use foreign key if the attributes of the one table have a unique id and foreign key will be identified when the other attributes are in the other table. Each attributes connects in performing every process.
Figure 6: Entity Relationship Diagram
Presentation, Analysis And Interpretation Of Data
This chapter shows the results of the User’s Survey conducted for the system to the ABC Registrar personnel’s and the student’s.
Presentation
The proponents demonstrate the system’s functionality to the randomly selected respondents. The proponents observed the respondents on how they response to the system. The respondents were evaluated using the User Acceptance Survey in order for the respondents to distinguish the level of acceptability, efficiency and effectiveness of the proposed system.
Data Analysis
This section presents the analysis of the data collected and gathered from the respondents of ABC Registrar personnel’s and the student’s.
Characteristics of the Respondents
| Respondents | Frequency |
| Registrar’s / Registrar’s Staff | 5 |
| CHMSC-FT Students | 1788 |
Table 5.0: Frequency of Respondents
The population composed of the ABC Registrar’s personnel and students. The proponent got three hundred twenty-five respondents from the registrar’s personnel and student.
Table 5.0 shows the number of respondent who have answered the User-Acceptability Survey. The researchers got a total number of 330 respondents.
Reliability Testing
The data collected by the proponents have undertaken reliability testing an acceptable approach through using the Yamanes Formula in order.
Yamanes Formula:
n = Sample size
N = Population size
e = level of precision 0.05 % (5%)
Solution:
Registrar’s
This solution explains the summation of getting the sample size (n) of the population that will be taking the user acceptance survey. Where N=5 divided by 1+5 multiplied by 0.0025 as (e) or the level of precision. As the proponents gets the (e), it is divided to 5 as the total population size (N). The result was 5 for the sample size of the population (n).
Solution:
Student’s
This solution explains the summation of getting the sample size (n) of the population that will be taking the user acceptance survey. Where N=1788 divided by 1+1788 multiplied by 0.0025 as (e) or the level of precision. As the proponents gets the (e), it is divided to 1788 as the total population size (N). The result was 327 for the sample size of the population (n).
Interpretation of Data
| Range Of Mean | Verbal Interpretation |
| 4.21-5.00 | Very Satisfied |
| 3.41-4.20 | Satisfied |
| 1.81-2.60 | Dissatisfied |
| 1.00-1.80 | Very Dissatisfied |
The instrument wished to access the perception of the users in terms of five (5) categories namely: Effectiveness, Efficiency, Quality, Timeliness and Productivity. The first category was composed of four (4) items, the second category was composed of three (3) items, and the third, fourth and last categories were composed of four (4) items.
Effectiveness
Table 5.2: Survey Result – Effectiveness
| EFFECTIVENESS | |||||
| QUESTION 1 | QUESTION 2 | QUESTION 3 | QUESTION 4 | TOTAL MEAN | |
| Mean | 4.4455 | 4.4424 | 4.5121 | 4.4455 | 4.4614 |
| N | 330 | 330 | 330 | 330 | 330 |
| Std. Deviation | .62743 | .63199 | .61008 | .62257 | .49602 |
Table 5.2 shows that the user’s survey result for the effectiveness of the system came back with a total mean of 4.4614 which interpret that the users were very satisfied with the system’s effectiveness after testing it.
The respondents stated that the proposed system ABC Online Queueing System meet the desired result and it produced the desired output. They also stated that the system is effective, it means it has an intended or expected outcome.
Efficiency
Table 5.3: Survey Result – Efficiency
| EFFICIENCY | ||||
| QUESTION 1 | QUESTION 2 | QUESTION 3 | TOTAL MEAN | |
| Mean | 4.4818 | 4.4970 | 4.3515 | 4.4434 |
| N | 330 | 330 | 330 | 330 |
| Std. Deviation | .65324 | .65348 | .70436 | .52912 |
Table 5.3 shows that the users survey result for the system’s efficiency came back with a total mean of 4.4434 which interpret that the users were very satisfied with the efficiency of the system after testing it.
The respondents stated that the system ABC Online Queueing System, has the ability to avoid wasting materials, energy, efforts, and time in generating and recording statistical reports. In a more general sense, the system ABC Online Queueing System, has the ability to do things well, successfully, and without waste.
Quality
Table 5.4: Survey Result – Quality
| QUALITY | |||||
| QUESTION 1 | QUESTION 2 | QUESTION 3 | QUESTION 4 | TOTAL MEAN | |
| Mean | 4.4758 | 4.5182 | 4.5303 | 4.4939 | 4.5045 |
| N | 330 | 330 | 330 | 330 | 330 |
| Std. Deviation | .62449 | .60492 | .63389 | .62978 | .49655 |
Table 5.4 shows that the user’s survey result for the system’s quality came back with a total mean of 4.5045 which interpret that the users were very satisfied with the system’s quality after testing it.
The respondents stated that the system ABC Online Queueing System, meet the standards of the users in terms of its degree of excellence.
Timeliness
Table 5.5: Survey Result – Timeliness
| TIMELINESS | |||||
| QUESTION 1 | QUESTION 2 | QUESTION 3 | QUESTION 4 | TOTAL MEAN | |
| Mean | 4.4788 | 4.5091 | 4.5485 | 4.5636 | 4.5250 |
| N | 330 | 330 | 330 | 330 | 330 |
| Std. Deviation | .67150 | .60008 | .63754 | .62170 | .49306 |
Table 5.5 shows that the user’s survey result for the system’s timeliness came back with a total mean of 4.5250 which interpret that the users were very satisfied with the system’s quality after testing it.
The respondents stated that the system ABC Online Queueing System, has the quality in generating and recording statistical reports in favorable or useful time.
Productivity
Table 5.6: Survey Result – Productivity
| PRODUCTIVITY | ||||
| QUESTION 1 | QUESTION 2 | QUESTION 3 | TOTAL MEAN | |
| Mean | 4.4848 | 4.5788 | 4.5242 | 4.5293 |
| N | 330 | 330 | 330 | 330 |
| Std. Deviation | .62962 | .60003 | .62449 | .50394 |
Table 5.6 shows that the user’s survey result for the system’s productivity came back with a total mean of 4.5293 which interpret that the users were very satisfied with the system’s quality after testing it.
The respondents stated that the system ABC Online Queueing System has the ability to produce a desired result. They measured the ratio of output to inputs used in a production process, i.e. output per unit of input.
Overall
Table 5.7: Survey Result – Overall
| Overall | ||
| Mean | N | Std. Deviation |
| 4.6394 | 330 | .54602 |
Summary Of Findings, Conclusions And Recommendations
This chapter presents the summary of the findings, and the conclusions and the recommendations for the system study.
Summary of Findings
This study was conducted for the purpose of designing an queueing system for ABC Campus, to objectively result to a faster, efficient, and effective service to the students. The descriptive method of research was utilized and the survey technique was used for gathering date. A questionnaire served as an instrument for the collection of data.
The proponents conducted a survey to the employees of the barangay. There were 330 employees in their department, one personnel in-charge, four active staff and 325 students. The survey was conducted after the system had all the requirements, functionalities and features embedded.
The findings suggested that on the level of the user’s experience in terms of effectiveness of the system a mean score of 4.4424
was obtained, interpreted as “satisfied”. As to the experience of the user in the efficiency category, it obtained a mean of 4.4455, it interpreted “very satisfied”. On its system quality category, the users, it raked a mean of 4.4614 interpreted as “very satisfied”. On timeliness category, the users gave a mean of 4.5250 interpreted as “very satisfied”. On productivity category the user gave a mean of 4.5293 interpreted as “very satisfied”. And on the last category which is the efficiency category the users gave it a mean 4.4434 interpreted as “very satisfied”. In overall, the systems rating is collected a mean of 4.6394 is interpreted as “very satisfied” rating.
Conclusion
The proponents conclude that the system is fully operational and dynamic, as of the sum data gathered. This condition is on the premise that it has addressed the efficiency and effectiveness of the system to serve a student of the firm after the thorough system study.
Recommendations
As the proponents had made an information system for the ABC, the system shall have maintenance for every 6 months to maintain and update its functions and also for the security of its databases.
REFERENCES
“Customer Queue Management System , Leading Enterprise Software with SMS Notifications and Online Appointments.” Accessed August 30, 2018. https://queuerite.com/.
(n.d.). Retrieved from http://thesis.dlsud.edu.ph/2732/1/CEN%20009%202014.pdf
“Pattawi, J. (2018, March 17). “II.RELATED LITERATURE REVIEW.” . Retrieved from http://www.academia.edu/19723729/Chapter_2_Literature_Review
Backer, Alejandro, and Timothy Ross McCune. Wireless remote queuing system and method. United States US20080133283A1, filed November 16, 2007, and issued June 5, 2008. https://patents.google.com/patent/US20080133283/en.
AL-Jumaily, Ahmed S. A., and Dr Huda K. T. AL-Jobori. “Automatic Queuing Model for Banking Applications.” International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications (IJACSA) 2, no. 7 (2011). https://doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2011.020702.
Uddin, Md.Nasir, NA Nithe, and SZ Ahmed. “Automated Queue Management System.” Global Journal of Management and Business Research 16 (December 31, 2015): 51–58.


Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.