Retail Store Management System Capstone Project Document
Introduction
Development of large software system is extremely complex activity full of various opportunities to introduction errors. Software Engineering is the discipline that attempts to provide method to handle this complexity, enabling us to produce reliable system software with maximum productivity.
It was felt that it is important and very instructive, not only to learn the principles of software engineering but also apply them to a software development project so that all aspects of development and be clearly seen on project.
Software engineering is activity starts from requirements analysis and ends with testing and implementation.
This project is designed to manage a Retail Store System. In This project VB 6.0 is use as front-end and Oracle use as backend.
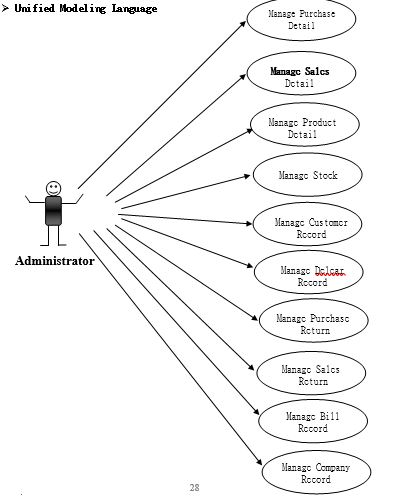
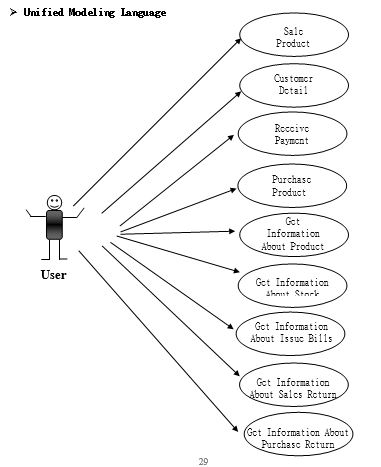
- In this project we can manage:
- Purchase Record,
- Purchase Return Record,
- Purchase Detail,
- Sales Record,
- Sales Return Record,
- Sales Details,
- Product Record,
- Categories Detail,
- Dealer Record,
- Customer Record,
Objective of the Project
Main objective of this project is using information technology we can easily manage the Retail Store Management System. Now a day, in world every work is require fast. In short time we can require bulk of work, and also manage many documentation records.
In Retail Store different-different products are purchase from dealer and sale to the customer. Such Product as: Stationeries, Grocery product, Cosmetics, etc. In this every customer have their different- different requirement. Suppose we have to maintain the sales record properly then retail store requires a good system which are keep the customer record,
Bill Number record, Bill date record, grand total.
Earlier sales record was done manually by documentation. It involves lot of man power. Suppose we want to search any record then lot of problem was faced by retail store. Day by day records increases. Then many problems were come. And some time we want instant record then it difficult to find.
When sales inquiry about product then we have to maintain inquiry record. We have to inform all type of courses, their fees to students. After some time we want to see this record then more difficult to find a this kind record in manual system
Various types of Grocery products, its cost, price are such kind of record. These records are used at the time of Sales of product to the customer. When Customer paid their Payment then keep the record of Payment & update the record. If we want to a record of customer as their Product wise then it was tedious job.
Customer payment record was most important to maintain properly such as who are paid, when paid, how much paid, their outstanding amount, their paid amount etc… Suppose we have to see every customer payment status then it is more difficult to collect a kind of record.
In every product many customers take their purchase. If we have to maintain the customer billing record properly then store requires a good system which is kept the billing records of customer.
Same as this many other tasks are also available such as Sales record, purchase record etc. So in manual system records maintain processes are more difficult. With the use of this project store can maintain their customer record easily.
Project Category
This project Category is Expert System which are managed the Retail store processes. In this system we can store products record.
System Configuration
Hardware Requirements
- Processor – Intel® Pentium® 4
- Processor speed – 2.50 GHZ
- Hard disk – Minimum 40 GB
- Main Memory – 1 GB
- Monitor – TFT (thin Film transistor)
- Keyboard – Multimedia
- Mouse – Optical or Scroll Mouse
- CD Drive – DVD writer
Software Requirements
- Front end Language: – Visual Basic 6.0
- Back end Language: – SQL Server
- Operating System – Windows XP
Brief Introduction About Visual Basic 6.0
VISUAL BASIC is a high level programming language which evolved from the earlier DOS version called BASIC. BASIC means Beginners’ All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code. It is a very easy programming language to learn. The code looks a lot like English Language. Different software companies produced different versions of BASIC, such as Microsoft QBASIC, QUICKBASIC, GWBASIC, IBM BASICA and so on. However, people prefer to use Microsoft Visual Basic today, as it is a well developed programming language and supporting resources are available everywhere. Now, there are many versions of VB exist in the market, the most popular one and still widely used by many VB programmers is none other than Visual Basic 6. We also have VB.net, VB2005, VB2008 and the latest VB2010. Both Vb2008 and VB2010 are fully object oriented programming (OOP) language.
VISUAL BASIC is a VISUAL and events driven Programming Language. These are the main divergence from the old BASIC. In BASIC, programming is done in a text-only environment and the program is executed sequentially. In VB, programming is done in a graphical environment. In the old BASIC, you have to write program code for each graphical object you wish to display it on screen, including its position and its color. However, In VB , you just need to drag and drop any graphical object anywhere on the form, and you can change its color any time using the properties windows.
On the other hand, because the user may click on a certain object randomly, so each object has to be programmed independently to be able to response to those actions (events). Therefore, a VB Program is made up of many subprograms, each has its own program code, and each can be executed independently and at the same time each can be linked together in one way or another.
Visual Basic is the third-generation event-driven programming language and integrated development environment (IDE) from Microsoft for its COM programming model. Visual Basic is relatively easy to learn and use.
Visual Basic was derived from BASIC and enables the rapid application development (RAD) of graphical user interface (GUI) applications, access to databases using Data Access Objects, Remote Data Objects, or ActiveX Data Objects, and creation of ActiveX controls and objects. Scripting languages such as VBA and VBScript are syntactically similar to Visual Basic, but perform differently.
A programmer can put together an application using the components provided with Visual Basic itself. Programs written in Visual Basic can also use the Windows API, but doing so requires external function declarations.
- Language Features
Like the BASIC programming language, Visual Basic was designed to be easily learned and used by beginner programmers. The language not only allows programmers to create simple GUI applications, but can also develop complex applications. Programming in VB is a combination of visually arranging components or controls on a form, specifying attributes and actions of those components, and writing additional lines of code for more functionality. Since default attributes and actions are defined for the components, a simple program can be created without the programmer having to write many lines of code. Performance problems were experienced by earlier versions, but with faster computers and native code compilation this has become less of an issue.
Although programs can be compiled into native code executables from version 5 onwards, they still require the presence of runtime libraries of approximately 1 MB in size.
This runtime is included by default in Windows 2000 and later, but for earlier versions of Windows like 95/98/NT it must be distributed together with the executable.
Forms are created using drag-and-drop techniques. A tool is used to place controls (e.g., text boxes, buttons, etc.) on the form (window).
Controls have attributes and event handlers associated with them. Default values are provided when the control is created, but may be changed by the programmer. Many attribute values can be modified during run time based on user actions or changes in the environment, providing a dynamic application. For example, code can be inserted into the form resize event handler to reposition a control so that it remains centered on the form, expands to fill up the form, etc. By inserting code into the event handler for a keypress in a text box, the program can automatically translate the case of the text being entered, or even prevent certain characters from being inserted.
Visual Basic can create executables (EXE files), ActiveX controls, or DLL files, but is primarily used to develop Windows applications and to interface database systems. Dialog boxes with less functionality can be used to provide pop-up capabilities. Controls provide the basic functionality of the application, while programmers can insert additional logic within the appropriate event handlers. For example, a drop-down combination box will automatically display its list and allow the user to select any element. An event handler is called when an item is selected, which can then execute additional code created by the programmer to perform some action based on which element was selected, such as populating a related list.
Alternatively, a Visual Basic component can have no user interface, and instead provide ActiveX objects to other programs via Component Object Model (COM). This allows for server-side processing or an add-in module.
The language is garbage collected using reference counting, has a large library of utility objects, and has basic object oriented support. Since the more common components are included in the default project template, the programmer seldom needs to specify additional libraries. Unlike many other programming languages, Visual Basic is generally not case sensitive, although it will transform keywords into a standard case configuration and force the case of variable names to conform to the case of the entry within the symbol table. String comparisons are case sensitive by default, but can be made case insensitive if so desired.
The Visual Basic compiler is shared with other Visual Studio languages (C, C++), but restrictions in the IDE do not allow the creation of some targets (Windows model DLLs) and threading models.
- Characteristics
- By default, if a variable has not been declared or if no type declaration character is specified, the variable is of type Variant. However this can be changed with Deftype statements such as DefInt, DefBool, DefVar, DefObj, DefStr. There are 12 Deftype statements in total offered by Visual Basic 6.0. The default type may be overridden for a specific declaration by using a special suffix character on the variable name (# for Double, ! for Single, & for Long, % for Integer, $
For String, and @ for Currency) or using the key phrase As (type). VB can also be set in a mode that only explicitly declared variables can be used with the command Option Explicit.
- Multiple assignments available in C language is not possible. A = B = C does not imply that the values of A, B and C are equal. The boolean result of “Is B = C?” is stored in A. The result stored in A would therefore be either false or true.
About The Structured Query Language (SQL)
The Structured Query Language (SQL) is the set of instructions used to interact with a relational database. In fact, SQL is the only language that most databases actually understand. Whenever you interact with such a database, the software translates your commands (whether they are mouse clicks or form entries) into SQL statement that the database knows how to interpret. SQL has three major components: the Data Manipulation Language (DML), the Data Definition Language (DDL), and the Data Control Language (DCL).
SQL is a programming language designed for managing data in relational database management systems (RDBMS).
Originally based upon relational algebra and tuple relational calculus, its scope includes data insert, query, update and delete, schema creation and modification, and data access control.
SQL was one of the first commercial languages for Edgar F. Codd‘s relational model, as described in his influential 1970 paper, “A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks”. Despite not adhering to the relational model as described by Codd, it became the most widely used database language. Although SQL is often described as, and to a great extent is, a declarative language, it also includes procedural elements. SQL became a standard of the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in 1986, and of the International Organization for Standards (ISO) in 1987. Since then the standard has been enhanced several times with added features. However, issues of SQL code portability between major RDBMS products still exist due to lack of full compliance with, or different interpretations of the standard. Among the reasons mentioned are the large size, and incomplete specification of the standard, as well as vendor lock-in.
The SQL language is subdivided into several language elements, including:
- Clauses, which are constituent components of statements and queries. (In some cases, these are optional.)
- Expressions, which can produce eitherscalar values or tables consisting of columns and rows of data.
- Predicates, which specify conditions that can be evaluated to SQLthree-valued logic (3VL) or Boolean (true/false/unknown) truth values and which are used to limit the effects of statements and queries, or to change program flow.
- Queries, which retrieve the data based on specific criteria. This is the most important element ofSQL.
- Statements, which may have a persistent effect on schemata and data, or which may control transactions, program flow, connections, sessions, or diagnostics.
SQL statements also include the semicolon (“;”) statement terminator. Though not required on every platform, it is defined as a standard part of the SQL grammar.
- Insignificant whitespaceis generally ignored in SQL statements and queries, making it easier to format SQL code for readability.
Queries:-
The most common operation in SQL is the query, which is performed with the declarative SELECT statement. SELECT retrieves data from one or more tables, or expressions. Standard SELECT statements have no persistent effects on the database. Some non-standard implementations of SELECT can have persistent effects, such as the SELECT INTO syntax that exists in some databases.
Queries allow the user to describe desired data, leaving the database management system (DBMS) responsible for planning, optimizing, and performing the physical operations necessary to produce that result as it chooses.
A query includes a list of columns to be included in the final result immediately following the SELECT keyword. An asterisk (“*”) can also be used to specify that the query should return all columns of the queried tables. SELECT is the most complex statement in SQL, with optional keywords and clauses that include:
- TheFROM clause which indicates the table(s) from which data is to be retrieved. The FROM clause can include optional JOIN sub clauses to specify the rules for joining tables.
- TheWHERE clause includes a comparison predicate, which restricts the rows returned by the query. The WHERE clause eliminates all rows from the result set for which the comparison predicate does not evaluate to True.
- TheGROUP BY clause is used to project rows having common values into a smaller set of rows. GROUP BY is often used in conjunction with SQL aggregation functions or to eliminate duplicate rows from a result set. The WHERE clause is applied before the GROUP BY
- TheHAVING clause includes a predicate used to filter rows resulting from the GROUP BY Because it acts on the results of the GROUP BY clause, aggregation functions can be used in the HAVING clause predicate.
- TheORDER BY clause identifies which columns are used to sort the resulting data, and in which direction they should be sorted (options are ascending or descending). Without an ORDER BY clause, the order of rows returned by an SQL query is undefined.
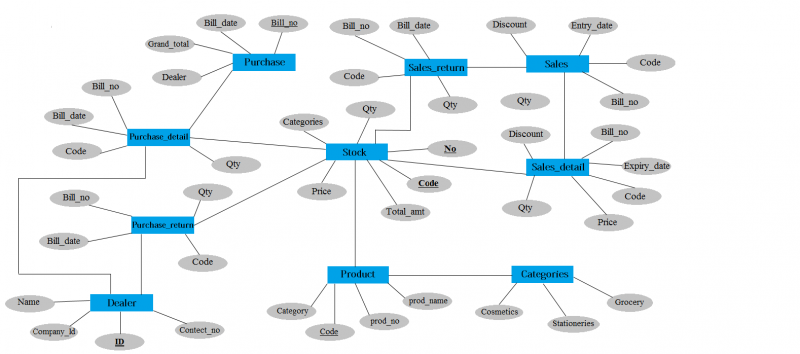
Entity Relationship Diagram
Model was introduced by P.P Chen. Entity-relationship is a detailed, logical representation of the entities, associations & data elements for an organization or business area. This technique is used in database design that helps to describe how entities in an enterprise are related to one another. E-R model for the data uses three features to describe data.
ERD displays & indicate the relationship between tables.
Database Tables
- Table Name:- Categories Primary Key:- Category
| No. | Column Name | Data Type | Description |
| 1. | Category | Varchar(20) | Primary Key(A.I.) |
| 2. | Cosmetics | Varchar(100) | To Store Cosmetics Product |
| 3. | Stationary | Varchar(100) | To Store Stationary Product |
| 4. | Grocery | Varchar(100) | To Store Grocery Product |
- Table Name:- Product Primary Key:- code
| No. | Column Name | Data Type | Description |
| 1. | Prod_No | Smallint | Product Number |
| 2. | Code | Smallint | To Store Product Code (Primary Key ) |
| 3. | Prod_Name | Varchar(50) | To Store the Product Name |
| 4. | Category | Varchar(20) | Foreign Key of categories |
- Table Name:- Dealer Primary Key:- ID
| No. | Column Name | Data Type | Description |
| 1. | ID | Smallint | Primary Key(A.I.) |
| 2. | Name | Varchar(25) | To Store the Dealer Name |
| 3. | Contect_no | Smallint | To Store the Dealer Phone |
- Table Name:- Purchase Primary Key:- Bill_No
| No. | Column Name | Data Type | Description |
| 1. | Bill_No | Smallint | Primary Key (A.I.) |
| 2. | Bill_Date | DateTime | To Store Purchase Bill Date |
| 3. | ID | Smallint | Foreign Key of Dealer |
| 4. | Grand_Total | Smallint | To Store the Grand Total |
- Table Name:- Purchase_Detail
| No. | Column Name | Data Type | Description |
| 1. | Bill_No | Smallint | Foreign Key Of Purchase |
| 2. | Code | Smallint | Foreign Key of Product |
| 3. | Qty | Smallint | To Store Purchase Quantity |
| 4. | Bonus | Smallint | To Store Bonus Product From Dealer |
| 5. | Discount | Smallint | To Store Discount on Product From Dealer |
| 6. | Price | Smallint | Product Price |
| 7. | Expiry_Date | DateTime | Product Expiry Date |
- Table Name:- Purchase_Return
| No. | Column Name | Data Type | Description |
| 1. | Bill_No | Smallint | Foreign Key Of Purchase |
| 2. | Bill_Date | DateTime | Purchase Bill Date |
| 3. | Code | Smallint | Foreign Key Of Product |
| 4. | Qty | Smallint | To Store Return Product Quantity |
- Table Name:- Sales Primary Key :- Bill_No
| No. | Column Name | Data Type | Description |
| 1. | Bill_No | Smallint | Primary Key(A.I.) |
| 2. | Bill_Date | DateTime | To Store Sale Bill Date |
| 3. | Cust_Name | Varchar(100) | To Store the Customer Name |
| 4. | Grand_Total | Smallint | To Store Sale Bill Total |
- Table Name:- Sales_Detail
| No. | Column Name | Data Type | Description |
| 1. | Bill_No | Smallint | Foreign Key Of Sales |
| 2. | Code | Smallint | Foreign Key Of Product |
| 3. | Qty | Smallint | Sale Quantity |
| 4. | Price | Smallint | Store Product Price |
| 5. | Discount | Smallint | Discount On Selling |
| 6. | Expiry_Date | DateTime | Product Expiry Date |
- Table Name:- Sales_Return
| No. | Column Name | Data Type | Description |
| 1. | Bill_No | Smallint | Foreign Key Of Sales |
| 2. | Bill_Date | DateTime | Store Sale Bill Date |
| 3. | Code | Smallint | Foreign Key Of Product |
| 4. | Qty | Smallint | Sale Quantity |
- View Name:- Stock
| No. | Column Name | Data Type | Description |
| 1. | No | Smallint | No Of Product |
| 2. | Code | Smallint | Product Code |
| 3. | Category | Varchar(20) | Store Category Of Product |
| 4. | Qty | Smallint | Stock Of Product |
| 5. | Price | Smallint | Average Price |
| 6. | Tatal_Amt | Int | Total Of Price * Qty |
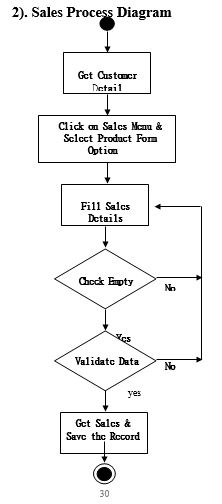
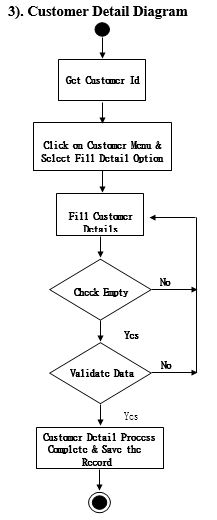
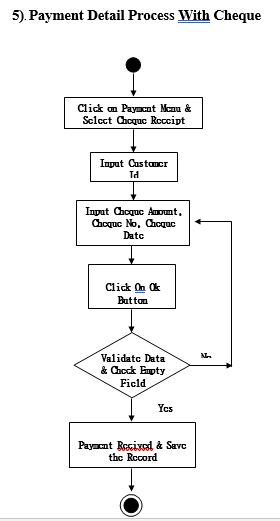
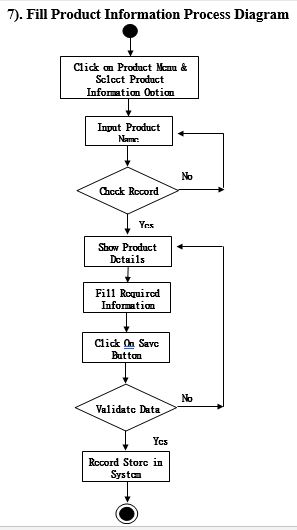
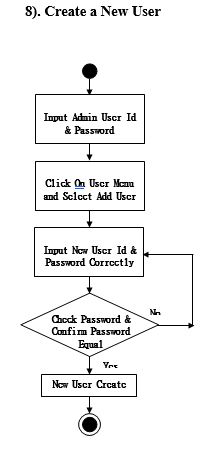
Process Model
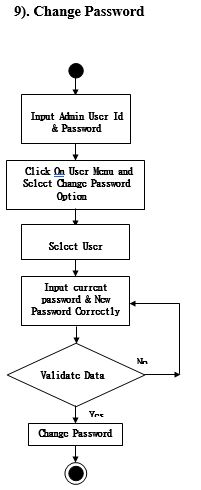
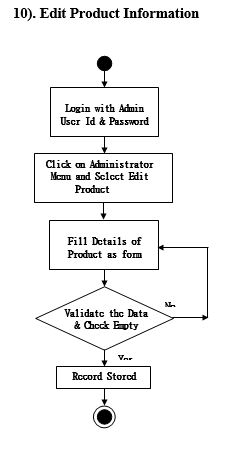
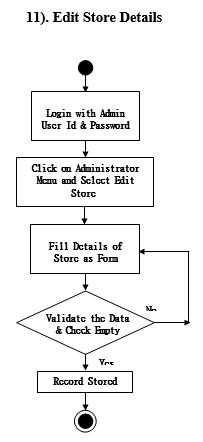
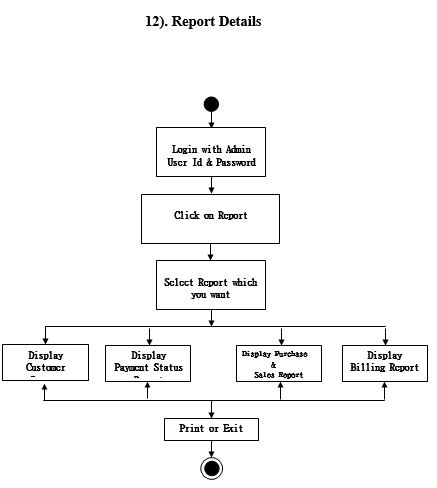
Activity Diagram
Data Flow Diagram
Data Flow Diagram (abbreviated as DFD) was introduced by De Marco (1978) and Gane and Sarson (1979). A data flow diagram models a system by using external entities from which data flows to a process which transforms the data and creates output data flows which goes to other processes or external entities or data stores.
The main merit of DFD is that it can provide an overview of what data a system would process, what transformations of data are done, what data are stored and which stored data are used, and where the result flows.
A data flow diagram (DFD) is a graphical representation of the “flow” of data through an information system, modelling its process aspects. Often they are a preliminary step used to create an overview of the system which can later be elaborated.[2] DFDs can also be used for the visualization of data processing (structured design).
A DFD shows what kinds of data will be input to and output from the system, where the data will come from and go to, and where the data will be stored. It does not show information about the timing of processes, or information about whether processes will operate in sequence or in parallel (which is shown on a flowchart).
Good Conventions In Developing DFD’S :-
Data Flow diagrams serve the dual purpose of specifying what data are needed for processing and as documentation of what procedures transform data.
A good Data Flow Diagram should not have the following:-
- Loops.
- A process, which is a poor decision.
- A Data Flow split into flows with different names and meanings.
- Crossing Lines.
A good Data Flow Diagram should have the following:-
- Process names, data stores names, and data flow names must be meaningful in the context of the problem.
- DFD’s must be developed top down with lower levels giving more details.
- Data should be conserved.
- Data flows should not act as signals to activate or initiate processes.
Modules
- Main Function module
- Contain Main function. So , Program execution start from main function
- Database Connection module
- Database connection variables and connection strings for connect to the SQL database. Also check for database connection is active or not
- Number To Text Convert module
- This module is use for convert Numeric value to Word. It’s catch value through parameter and return Number to Word.
Reports
- Product List Report
- Dealer List Report
- Purchase Report
- Purchase Return Report
- Sales Report
- Sales Return Report
- Expire Medicines Report
- Stock Report
Software Testing
Testing
Once the program code is designed and implemented, some testing technique will be used to ensure the program function correctly.
Unit Testing
Individual modules will be tested against the specification and design to confirm their correct operation.
Integration Testing
Several units will be tested together to see how they interact and to confirm whether their overall function is performed correctly. This testing will apply to each of the main section of code; the use interface, data processing, etc.
System Testing
The entire system is tested against the specification to check it meets the project’s requirements.
Objective
- Testing is a process of the executing a program with the intent of finding an error.
- A good test case is one that has high probability of finding an as yet undiscovered error.
- A successful test is one that uncovers an as yet undiscovered Error.
Principles
- All tests should be traceable to customer requirement.
- Tests should be implemented long before test begins.
- Testing should begin “in the small” and progress towards testing “in the large”
- Expansive testing is not possible.
- To be most effective, an independent third party should conduct testing.
Time Line Chart
| TASK | WEEK1 | WEEK2 | WEEK3 | |||||||||||||
| 1 | Identify needs & benefit | |||||||||||||||
| 1.1 | Identify pro constrain | |||||||||||||||
| 1.2 | Identify Objective | |||||||||||||||
| 1.3 | Gathering requirements | |||||||||||||||
| 1.4 | Analysis requirements | |||||||||||||||
| Milestone : Requirements Complete | ||||||||||||||||
| 2 | Concept Planning | |||||||||||||||
| 2.1 | Research on exist s/w | |||||||||||||||
| 2.2 | Define task | |||||||||||||||
| 2.3 | Define i/o function | |||||||||||||||
| 2.4 | Divide in to module | |||||||||||||||
| Milestone : Concept planning complete | ||||||||||||||||
| 3 | S/w requirements specification | |||||||||||||||
| 3.1 | UML diagram | |||||||||||||||
| Milestone : SRS design complete | ||||||||||||||||
| 4 | Design | |||||||||||||||
| 4.1 | Data Design | |||||||||||||||
| 4.2 | Architectural design | |||||||||||||||
| Task | Week 4 | Week5 | Week6 | |||||||||||||
| 4.3 | User interface design | |||||||||||||||
| 4.3.1 MDI form, Login Form design | ||||||||||||||||
| 4.3.2 Customer Form design | ||||||||||||||||
| 4.3.3 Payment receipt design | ||||||||||||||||
| 4.3.4 Stock record form design | ||||||||||||||||
| 4.3.5 Sales record from design | ||||||||||||||||
| 4.3.6 other form design | ||||||||||||||||
| Milestone : Design Module Complete | ||||||||||||||||
| 5 | Res/Rej module | |||||||||||||||
| 5.1 | Component level diag | |||||||||||||||
| 5.2 | Coding | |||||||||||||||
| 5.3 | Testing | |||||||||||||||
| Milestone : Res/Rej module complete | ||||||||||||||||
| 6 | User Register | |||||||||||||||
| 6.1 | Component design | |||||||||||||||
| 6.2 | Coding | |||||||||||||||
| 6.3 | Testing | |||||||||||||||
| Milestone : Registration module | ||||||||||||||||
| 7 | Functional Analysis | |||||||||||||||
| 7.1 | Component level design | |||||||||||||||
| 7.2 | Coding | |||||||||||||||
| 7.3 | Testing | |||||||||||||||
| Milestone Analysis module complete | ||||||||||||||||
| Week 7 | Week8 | ||||||||||
| 4.3 | System Design | ||||||||||
| Interface Design | |||||||||||
| Milestone Design Complete | |||||||||||
| Testing | |||||||||||
| Milestone : Testing Complete | |||||||||||
Scope of the project
This project has some limitations. These are as below
- Database backup and restore process is not included.
- Yearly Record and Monthly Status is not available.
- Last year Record find is not possible in this project.
- Staff salary and attendance could not maintain in this project.
- Student attendance is also not managed in this project.
- Total fees collection & Whole Branch Summary Report is not include in this.
Future Scope
All over limitations are tried to solve in my project. And try to best solve customer requirements.






Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.